The Ultimate Guide to Deemed Export GST Rate
- 9 Aug 24
- 18 mins
The Ultimate Guide to Deemed Export GST Rate
Key Takeaways
- Deemed Export GST Rate: Tailored rates promote domestic competitiveness in global markets.
- Eligibility Criteria: Specific conditions apply, including supplies against advance authorization and to EOUs.
- GST Refund Procedure: This involves filing Form GST RFD-01, attaching documentation, and receiving refunds post-verification.
- Compliance Challenges: Include complex documentation, delayed refunds, regulatory ambiguities, and compliance costs.
- Technology's Role: Digital platforms like GSTN, automated refunds, and e-way bills facilitate deemed export management.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India is important for businesses to cross the complex tax outlook efficiently. Deemed exports, a unique category within the GST framework, refer to transactions where goods supplied do not leave the country, and the payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in convertible foreign exchange.
This article explains the deemed export GST rate, presenting insights into eligibility, benefits, and compliance procedures to make the most out of this provision.
Deemed Export GST Rate
The GST framework has intricately defined rates for various categories, including deemed exports. The current GST rate for deemed exports aims to promote ease of doing business, ensuring that domestic suppliers engaging in deemed export transactions are not at a disadvantage.
By comparing these rates with those applicable to regular trade, businesses can understand the financial implications and plan their transactions accordingly.
As of my last update in April 2023, the GST rate on deemed exports in India generally aligns with the standard GST rates applicable to the goods or services being supplied. However, these rates can vary from 5% to 28%, depending on the category of goods or services.
Eligibility Criteria for Deemed Exports
Not all transactions qualify as deemed exports under the GST law. It is essential to know the eligibility criteria, including the necessary documentation and the specific categories of deemed exports recognized by the GST Council.
The eligibility criteria for deemed exports in India are outlined as follows, based on the information retrieved from the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) and other reliable sources:
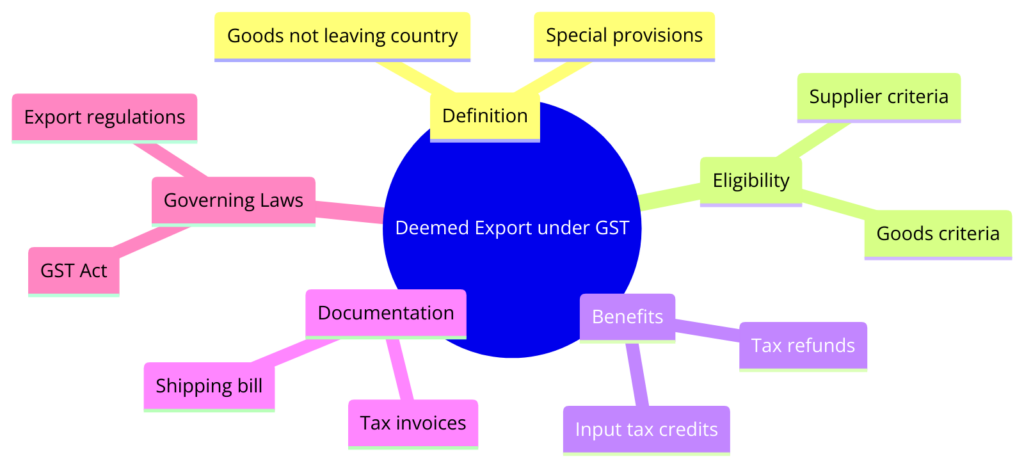
- Supply of goods by a registered person against Advance Authorization: Goods supplied against Advance Authorization (AA) are considered deemed exports. AA refers to an authorization issued to allow the import of inputs in physical form, which are then utilized to manufacture goods without payment of tax on imports, provided the finished goods are exported.
- Supply of goods by a registered person to an Export Oriented Unit (EOU) or Software Technology Park (STP) or Electronic Hardware Technology Park (EHTP) or Bio-Technology Park (BTP): Goods supplied to these units are treated as deemed exports, as these units operate under conditions similar to physical exports, with a focus on export production.
- Supply of capital goods by a registered person against Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Authorization: This involves the supply of capital goods to an exporter under the EPCG scheme, which allows import of capital goods for pre-production, production, and post-production at zero customs duty, conditional upon the fulfillment of trade obligations.
- Supply of goods by a registered person to projects funded by multilateral or bilateral agencies or funds as notified by the Government of India in the Ministry of Finance under International Competitive Bidding (ICB) in accordance with the procedures of those agencies or funds, where legal agreements provide for tender evaluation without including the customs duty.
- Supply of goods to a project for which the Ministry of Defense or a Ministry or Department of the Government of India has issued a "No Objection Certificate" for the import of such goods under ICB.
Benefits of Deemed Export Status
Deemed export status in India offers several benefits designed to promote exports and manufacturing within the country. These benefits are aimed at making domestic goods competitive in the global market and encouraging the production of goods for trade.
Here are the key benefits associated with deemed export status:
- Refund of GST Paid: Suppliers of deemed exports are eligible for a refund of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) paid on the goods supplied. This refund mechanism ensures that the tax burden does not add to the cost of goods intended for exports, making them more competitive in international markets.
- Advance Authorization Benefits: Suppliers can avail themselves of advance authorization for duty-free import of inputs that are physically incorporated in the trade product. This benefit reduces the cost of raw materials and inputs for the production of goods destined for trade.
- Exemption from Payment of GST on Inputs: Suppliers to deemed exports can obtain supplies of inputs required for the manufacture of trade goods without paying GST on such inputs under schemes such as the Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) scheme. This exemption further lowers the cost of production for exporters.
- Eligibility for Export Promotion Capital Goods Scheme: Suppliers can benefit from the EPCG scheme, which allows the import of capital goods for pre-production, production, and post-production at zero customs duty, subject to export obligation. This helps reduce the capital costs for exporters.
- Competitive Advantage: By reducing the cost of inputs and the tax burden, deemed export supply status gives suppliers a competitive advantage in the global market. This is crucial for maintaining and enhancing India's export competitiveness.
- Access to Global Markets: Deemed exports frequently work with international organizations to fund their projects or are a part of global supply chains. This status helps suppliers tap into international markets and projects, expanding their business reach.
- Eligibility for Special Economic Zone (SEZ) Supplies: Suppliers making supplies to SEZ units or developers for authorized operations are treated as deemed exports, providing them the benefits of duty drawbacks and tax refunds, which further enhance their competitiveness.
- Facilitation of Cash Flow: The refund of GST paid on deemed exports helps improve liquidity and cash flow for suppliers, enabling them to invest more in their production capacities and innovation.
Procedure for Claiming GST Refund
One of the most significant advantages of deemed export status is the ability to claim GST refunds. This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide on the refund process, including the documentation required, to ensure businesses can reclaim their dues without hassle
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Businesses can claim a refund of the input tax credit when the tax paid on inputs is more than the tax liability on the output. This scenario commonly arises in export businesses where the goods or services are zero-rated.
- Penalty: If there is any delay or discrepancy in claiming the GST refund, a penalty may be imposed. The penalty can be in the form of interest on the refund amount due from the due date of the claim until the date of the refund.
- Refund of Tax Paid: Taxpayers can claim a refund of tax paid in cases of trade of goods or services, excess payment due to mistake or inadvertence, and finalization of provisional assessment.
- Erroneous Refund: If a refund of tax paid has been issued erroneously, the taxpayer is liable to repay the amount along with interest. Procedures are in place to recover such refunds.
- Filing a Refund Claim: The process begins with the filing of a refund application in Form GST RFD-01 on the GST portal. This form should be filed within 2 years from the relevant date.
- Gathering of Refund Claims: All related documents supporting the claim, such as invoices, tax payment receipts, and bank account proof, must be gathered and submitted along with the application.
- Method of Refund: The refund can be processed either as a direct bank transfer to the claimant's account or, in some cases, as an adjustment against future tax liabilities.
- Refund Application: The application for a refund must be comprehensive, stating the reason for the refund, the period for which the refund is sought, and the amount of refund claimed.
- Refund Issues: Any issues related to the refund claim, such as discrepancies in the application or required documents, must be addressed promptly to avoid delays.
- Request of Refund: A formal request for refund, following the prescribed format and guidelines, initiates the refund process.
- Rules for Refunds: The GST law outlines specific rules and conditions under which refunds can be claimed. These include the time limit, documentation, and procedure.
- Time of Filing Refund: The refund claim must be filed within a stipulated period, generally 2 years from the relevant date, which varies depending on the type of refund.
- Deemed Export Supplies: Special provisions exist for refunds in cases of deemed exports, where goods supplied do not leave the country but are considered exports under GST laws.
- Export License: While not directly related to GST refunds, having an export license can facilitate smoother processing of refunds for export-related transactions.
- Export of Services: Refunds for the export of services require proof that the services were provided outside India, along with payment received in convertible foreign exchange.
- Penalty Sections: Specific sections of the GST law detail the penalties for non-compliance with refund procedures, including delays in filing or furnishing incorrect information.
Procedure for Claiming GST Refund
- Filing of Application: Submit Form GST RFD-01 electronically through the GST portal.
- Documentation: Attach all necessary documents, including invoices, proof of payment, and bank account details.
- Processing: The GST officer verifies the application within 15 days, and any discrepancies are the claimant's responsibility to fix.
- Grant of Refund: After successful verification, the refund is credited to the claimant's bank account within 60 days of the application date.
Impact of GST on Deemed Exports
GST has been perceived as a remarkable step towards generating a significant impact on various industries in our economy, including deemed exports. Deemed exports under GST refer to those transactions in which the goods supplied do not leave the country, and the payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in convertible foreign exchange, but they are treated as exports under GST laws for certain benefits.

- Eligibility for Refunds: One of the most significant impacts of GST on deemed exports is the eligibility for refunds of tax paid on supplies regarded as deemed exports. This provision ensures that the tax burden does not escalate the cost of goods supplied under deemed export categories, making them more competitive in the domestic market.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Suppliers of deemed exports can avail of input tax credit for the GST paid on inputs and input services used in making the supply. This feature helps reduce the cost of production and improves the cash flow for suppliers engaging in deemed exports.
- Streamlined Process: GST has streamlined the process for claiming refunds on the tax paid on inputs for deemed exports. The documentation and procedural requirements have been simplified, making it easier for businesses to claim refunds, thereby improving operational efficiency.
- Increased Compliance: While GST has brought in several benefits for deemed exports, it also comes with increased compliance requirements. Suppliers need to meticulously document their transactions, maintain proper records, and file returns timely to avail themselves of the benefits associated with deemed exports.
- Working Capital Impact: The mechanism for refund claims under GST, although streamlined, can still lead to working capital issues for suppliers. The time taken for the processing of refunds may impact the cash flow, especially for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) engaged in deemed exports.
- Clarity and Certainty: GST has provided clarity and certainty regarding the treatment of deemed exports. Clear guidelines and criteria define what constitutes deemed exports, the benefits available, and the procedure for availing of these benefits, reducing ambiguity and potential disputes.
- Competitive Advantage: By allowing refunds of GST paid on inputs used in the production of deemed exports, the policy helps reduce the cost of these supplies. This makes Indian suppliers more competitive against suppliers from countries where exports are taxed or where no such benefits are available.
Challenges in GST Compliance for Deemed Exports
Compliance with Goods and Services Tax (GST) for deemed exports presents several challenges for businesses in India. Deemed exports under GST are specific transactions that, although do not result in goods leaving the country, are recognized as exports for taxation purposes.
These transactions qualify for certain tax benefits, including refunds of the GST paid. However, navigating the compliance requirements for these benefits can be complex, and businesses often face various hurdles.
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Complex Documentation and Procedures | Businesses need to provide detailed documentation for deemed export benefits, including evidence of payment and contracts. | Increases administrative burden, leading to potential delays or errors in compliance. |
| Delayed Refunds | The process for receiving refunds of the GST paid on deemed exports can be lengthy. | Adversely affects cash flow, particularly for SMEs relying on timely refunds. |
| Ambiguities and Lack of Clarity | Ambiguities in what qualifies as a deemed export and changes in criteria can lead to confusion. | Results in disputes with tax authorities and potential penalties or denial of benefits. |
| Compliance Costs | Compliance with GST requirements for deemed exports can be costly, requiring investment in specialized software or professional advice. | Erodes tax benefits, affecting competitiveness. |
| Reconciliation Issues | Businesses must reconcile their GST filings with returns, which can be complex due to GST's multi-layered structure. | Leads to additional scrutiny, fines, or penalties for discrepancies. |
| Technological Challenges | The reliance on digital compliance and reporting for GST can be challenging for businesses with limited IT capabilities or in remote areas. | Hinder timely and accurate submission of documentation and filings, leading to non-compliance or delayed refunds. |
| Evolving Regulations | GST policies on deemed exports evolve, requiring businesses to stay informed and vigilant. | It makes it challenging to remain compliant, potentially leading to inadvertent errors or missed tax benefits. |
GST Rate Changes and Their Impact
For the economy, companies, and consumers, rates changes of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) can have a big impact. Adjustments like this are frequently used to control inflation, promote or inhibit the purchase of specific products and services, boost economic growth, and simplify tax administration.Here’s a general overview of the potential impacts of GST rate changes:
Impact on Businesses
- Cost of Production: A decrease in GST rates can reduce the cost of raw materials, thereby lowering production costs. Conversely, an increase in GST rates might elevate these costs.
- Pricing Strategies: Businesses often adjust their pricing strategies in response to GST rate changes to maintain or improve their market position. Lower GST rates can lead to reduced prices for consumers, potentially increasing demand.
- Compliance and Accounting: Any change in GST rates necessitates updates to accounting systems and processes. This can lead to temporary challenges in compliance and increased administrative costs, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
Impact on Consumers
- Consumer Prices: The most direct impact of GST rate changes on consumers is reflected in the prices of goods and services. Lower rates can make products and services more affordable, whereas higher rates may increase costs for consumers.
- Consumption Patterns: Changes in GST rates can influence consumer behavior, encouraging or discouraging the consumption of certain goods or services based on their new prices.
Impact on the Economy
- Inflation: GST rate adjustments can influence the overall price level in the economy. A general reduction in GST rates may help in controlling inflation, while an increase in rates could potentially contribute to inflationary pressures.
- Government Revenue: GST is a significant source of revenue for the government. Reducing GST rates on certain items might decrease tax revenue in the short term but could stimulate economic activity and consumption, potentially offsetting revenue losses. Conversely, increasing GST rates could boost immediate tax revenue but might suppress demand and economic growth.
- Sector-Specific Effects: The impact of GST rate changes can vary significantly across different sectors. Sectors where the GST rate is reduced could see growth due to increased demand, while sectors facing higher GST rates might experience a slowdown in demand.
Impact on Investment and Growth
- Investment Decisions: GST rate changes can affect investment decisions by businesses, influencing their expansion, diversification, or entry into new markets based on the revised tax implications.
- Economic Growth: Over the long term, strategic adjustments in GST rates can promote economic growth by enhancing the competitiveness of businesses, boosting exports, and attracting foreign investment.
Technology in Managing Deemed Exports: GST
Government initiatives and technological advancements have had a significant impact on the management of deemed exports under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. These elements play a crucial role in streamlining processes, enhancing compliance, and facilitating the smooth operation of businesses involved in deemed exports.
- Digital Platforms and GSTN: GSTN, a critical technological foundation for the entire GST system, is defined as such to make allowance for deemed exports. It made it possible with an online interface to fill out returns, process refunds, and comply with regulations through the digital connection thing, streamlining the manual paperwork and the labor-intensive.
- Automated Refund Mechanism: Technology has enabled an automated refund mechanism for deemed exports, where refunds are processed more quickly than in the pre-GST era. This automation helps address the liquidity challenges faced by exporters by speeding up the refund process.
- E-Way Bill System: The introduction of the electronic way (e-way) bill system under GST for the movement of goods has been beneficial for deemed exports. It ensures the seamless movement of goods within the country, with real-time tracking and reduced transit times.
- Integration with Customs and Export Promotion Schemes: The GST system and customs electronic commerce portals are technologically integrated, which makes it easier for deemed exports to get benefits under different export promotion schemes. This helps in reducing the compliance burden and facilitating smoother operations.
Government Initiatives and Support
- Clear Guidelines and Notifications: The government has issued clear guidelines and notifications regarding deemed exports under GST, providing clarity and certainty to businesses. This includes criteria for qualification, documentation requirements, and the refund process.
- Simplified Refund Process: Initiatives have been taken to simplify the refund process for deemed exports, including the introduction of a single application form for multiple tax periods and the allowance of provisional refunds to ease cash flow pressures on businesses.
- Capacity Building and Awareness: The government, through different entities, arranges seminars, workshops, and sessions for building the capacity of businesses and tax professionals in charge. It helps in providing the stakeholders with accurate and up-to-date data regarding the standards and consent guidelines for deemed export supply.
Conclusion
With tactics management, businesses engaged in deemed exports can address the complexities of the GST framework, thus optimizing their operations along with service delivery to consumers. The undefined future of technology and government policy will most definitely add to the efficiency and superiority of the procedures and make it more appealing to any party concerned.
Overall, the GST system, which is a result of deemed exports, contributes to the expansion of export-oriented production and trade, which in turn increases India's presence on the global market.
💡If you're encountering difficulties managing your GST payments, accessing Pice can significantly streamline your process. By leveraging such a tool, you can ensure accuracy, save time, and avoid penalties associated with late or incorrect payments. Start using Pice today to transform your GST management into a hassle-free experience.