Are there any exemptions or concessions for GST on milk chilling?
- 17 Aug 24
- 12 mins
Are there any exemptions or concessions for GST on milk chilling?
- What is milk chilling?
- Who is the Largest Exporter of Milk Chilling Plant?
- Importance of Milk Chilling
- GST Impact on Milk Chilling
- GST Exemption for Packing Services
- HSN Code for Milk Chilling Plant
- Impact on Tax Rates
- GST on Milk Chilling Services
- GST on Milk Storage Charges
- Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- The standard GST rate for milk chilling services in India is 18%.
- Certain agricultural-related milk chilling activities may qualify for GST exemptions or reduced rates.
- Dairy businesses can claim input tax credits for GST paid on non-exempt milk chilling services.
- Small dairy farmers face increased administrative duties under GST but benefit from the input tax credit system.
- Potential future changes to GST rates for dairy processes aim to simplify taxation and support industry growth.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has transformed the fiscal landscape of many industries in India, including the dairy sector. This article delves into the intricacies of GST as it applies to the milk chilling process, a critical component in maintaining the quality and safety of milk. Understanding these changes is vital for stakeholders in the dairy industry to manage costs effectively and comply with tax regulations.
What is milk chilling?
The activity of chilling milk is a crucial process in the dairy industry that involves rapidly cooling milk immediately after it is extracted from cows or other forms of animals. The primary purpose of this process is to reduce the milk's temperature to a safe level where the growth of harmful bacteria is minimized, preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of the milk.
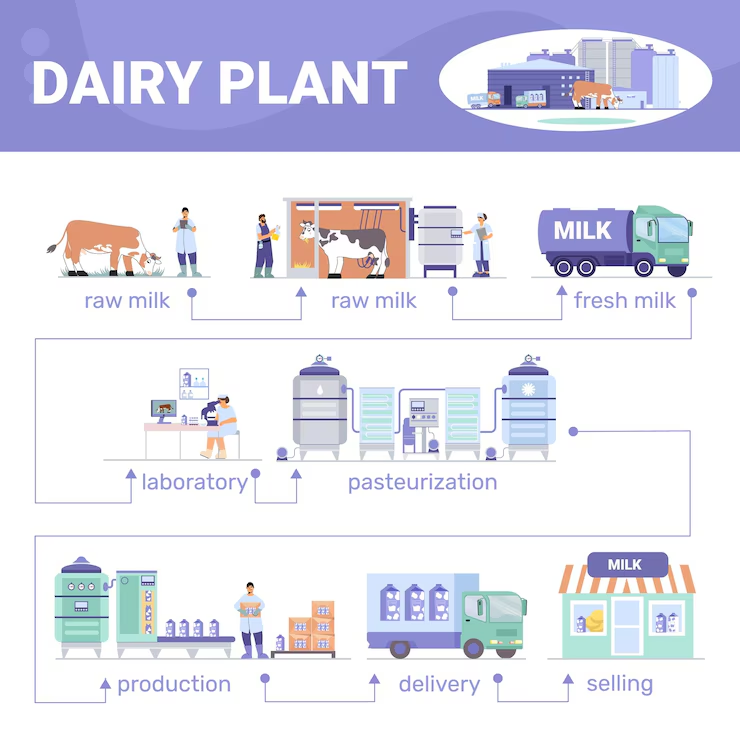
Typically, milk is chilled to about 4°C (39.2°F) or lower. This rapid cooling is achieved using various types of cooling systems, such as plate heat exchangers, bulk milk coolers, or in-line cooling systems.
ms. By chilling the milk quickly to the right temperature, the dairy industry ensures that the milk remains safe for consumption, retains its nutritional quality, and can be stored or transported over greater distances without spoiling.
This process is not only vital for maintaining public health but also enhances the efficiency of the dairy supply chain by reducing product waste and increasing the overall quality of dairy food products.
Who is the Largest Exporter of Milk Chilling Plant?
The global dairy industry relies heavily on technology for efficiency and quality preservation, with milk chilling plants being a cornerstone of this technological adoption. As of the latest data, Denmark-based companies like GEA Group and Tetra Pak are among the largest exporters of milk chilling plants.
These companies are renowned for their innovation and quality, attributes that position them as leaders in the market. Factors such as technological advancement, robust supply chains, and extensive service networks play pivotal roles in their market dominance.
Importance of Milk Chilling
Milk chilling is a critical procedure in the dairy industry, primarily because it directly influences the safety, quality, and shelf life of milk. The process involves quickly reducing the temperature of fresh milk soon after it is extracted to slow down microbial growth and enzymatic activity, which can spoil the milk.
Key Importance of Milk Chilling
- Safety and Public Health: By chilling milk to temperatures typically around 4°C (39.2°F) or lower, the growth of harmful bacteria such as Listeria, E. coli, and Salmonella is significantly inhibited. This is essential for preventing foodborne illnesses and ensuring the milk is safe for consumption.
- Quality Preservation: Rapid cooling helps maintain the sensory and chemical properties of milk, including taste, smell, and texture. It prevents the breakdown of milk fats and proteins, ensuring that the milk retains its natural flavor and nutritional value.
- Extended Shelf Life: Chilled milk can be stored for a longer period without significant degradation of quality. This extended shelf life is crucial for the logistical aspects of milk distribution, allowing it to be transported over longer distances from rural dairy farms to urban markets without spoiling.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have strict regulations regarding the storage and transportation temperatures of perishable products like milk. Milk chilling ensures compliance with these food safety standards, helping dairy businesses avoid legal issues and potential fines.
- Economic Benefits: By reducing spoilage, milk chilling contributes to lower operational losses for dairy farmers and milk processors. This efficiency boosts profitability and stability in the dairy industry’s supply chain.
- Consumer Satisfaction: Consistently providing high-quality, safe milk enhances consumer trust and satisfaction, which are critical for the brand reputation of dairy companies.
GST Impact on Milk Chilling
Under GST, services related to milk chilling are taxable. The tax rate applied can significantly affect the operational costs of dairy businesses that rely on milk chilling to maintain product quality. Here's a detailed look at the implications of GST on this critical dairy industry activity:
- GST Rates Applied to Milk Chilling
Milk chilling services are generally subject to a standard GST rate, which is currently set at 18%. This rate applies to the service of chilling milk, which includes the use of chilling equipment and energy consumption costs.
- Input Tax Credit for Dairy Farmers
One of the advantages of GST for the dairy industry is the ability to claim an input tax credit. Dairy businesses can claim credits on GST paid on inputs related to milk chilling, such as the purchase of chilling machinery and equipment. This can help mitigate the overall cost of the chilling process.
- Compliance and documentation
GST requires meticulous record-keeping and compliance with various tax procedures. For milk chilling services, this means maintaining accurate records of transactions, tax invoices, and GST filings. Compliance ensures that dairy businesses can effectively claim input tax credits and avoid penalties.
- Effect on Pricing and Profit Margins
The inclusion of GST on milk chilling services has led to adjustments in pricing strategies for dairy products. Businesses have to account for the added tax burden, which may affect their profit margins unless adequately managed through strategic pricing and cost controls.
- Impact on Small-scale Dairy Farmers
Small-scale farmers might find the GST system challenging due to its complexity and the need for digital compliance. However, understanding GST's impact on milk chilling can lead to better decision-making and potential financial benefits through tax credits.
While pasteurised milk is exempt from GST, other value-added milk products such as flavored milk, cheese, and yogurt are subject to GST. This differentiation is based on the view that basic necessities should be taxed differently from luxury or non-essential goods.
GST Exemption for Packing Services

Exemption Status
Packing services that are directly related to the agriculture sector, including the cultivation of plants, are generally exempt from GST. This exemption is designed to support the agricultural sector by reducing the operational costs associated with preparing products for sale and distribution.
- Scope of Exemption
The exemption typically covers retail packing services that are an integral part of the production and distribution process for agricultural products. This includes packing of raw materials of agricultural produce such as fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- Rationale Behind the Exemption
The primary aim of exempting such services from GST is to lower the cost burden on farmers and agricultural producers, encouraging more efficient and expanded production capacities.
By making these services more affordable, the government aims to enhance the competitiveness of Indian agricultural products in both domestic and international markets.
- Documentation and Compliance
While the service is exempt, businesses providing packing services to agriculture must maintain proper documentation to prove that their services meet the criteria for GST exemption. This includes records of the nature of the products packed and the relationship of the packing service to agricultural activity.
- Impact on the Agricultural Sector
This exemption plays a critical role in the agricultural value chain, allowing producers to invest more resources in improving product quality and expanding their market reach without the additional financial strain of GST on necessary services like packing.
HSN Code for Milk Chilling Plant
For milk chilling plants, which are essential in the dairy industry for cooling milk to prevent spoilage, the HSN code typically falls under a category that includes machinery used for the treatment of materials by a process involving a change of temperature, such as heating, cooking, roasting, distilling, rectifying, sterilizing, pasteurizing, steaming, drying, evaporating, vaporizing, condensing, or cooling.
Key Points about HSN Code for Milk Chilling Plants
- Classification and Code: Milk chilling cultivation plants are generally classified under the codes related to refrigeration or cooling machinery. The specific HSN code can vary depending on the exact nature of the equipment. Commonly, these can be classified under HSN 8418, which covers refrigerators, freezers, and other refrigerating or freezing equipment.
- Importance of Correct Classification
- GST Compliance: Correct classification ensures proper GST rates are applied, avoiding legal issues or penalties for misclassification.
- Taxation: Understanding which GST slab the equipment falls into helps in determining the total cost of procurement and operation, impacting budgeting and financial planning.
Impact on Tax Rates
The GST rates for milk chilling plants can vary. Milking machines and dairy machinery: Parts under HSN 8418 usually attract a standard GST rate, which might be around 18%. It is important for businesses to check the most current rates, as they can be subject to changes based on government policy.
- Documentation and Compliance
Proper documentation that includes the correct HSN code is crucial for smooth customs clearance for imported machinery and for audit processes in domestic transactions.
Using the right HSN code for milk chilling plants not only helps in ensuring compliance with the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act but also streamlines the process of tax filing and avoids complications during trade. Businesses involved in the manufacturing, import, or use of milk chilling plants must stay informed about the correct classification codes and applicable tax rates to manage costs effectively and maintain compliance with tax laws.
- Taxability of Milk Chilling & Storage Charges
The taxability of milk chilling and storage charges under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India plays a crucial role in the dairy industry, affecting everything from pricing strategies to operational logistics. Understanding how these services are taxed is essential for businesses to ensure compliance and optimal financial management.
GST on Milk Chilling Services

- Taxable Service
Milk chilling is considered a taxable service under GST. This includes the process of rapidly cooling milk at dairy farms or processing facilities to prevent the growth of microorganisms and preserve the milk's quality. The standard GST rate applied to milk chilling services is generally 18%. This rate is consistent across various states due to the centralized nature of the GST.
- Input Tax Credit
Dairy businesses can avail themselves of an input tax credit for the GST paid on services associated with milk chilling. This helps offset the GST liabilities on their output, making it a significant aspect of tax planning and management in the dairy sector.
GST on Milk Storage Charges
- Storage and Preservation
Milk storage and preservation services, which may include refrigerated warehousing and logistical support, are also taxable under GST.
Similar to chilling services, the typical GST rate for storage services is 18%. However, businesses need to review any specific notifications or amendments that might apply specific rates or exemptions under certain conditions.
- Considerations for Small Dairy Farmers
Small dairy farmers or smaller entities might struggle with the complexities of GST compliance. They need to ensure that they understand how to apply the tax rates correctly and how to claim their input tax credits effectively to manage costs.
- Impact of GST on Dairy Logistics
The inclusion of milk chilling and storage services under GST has implications for the cost structure of dairy logistics. Dairy processors and farmers must factor in these costs when pricing their products and negotiating supply contracts.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Proper documentation is crucial for compliance. This includes maintaining detailed invoices and records of all transactions related to milk chilling and storage that attract GST.
- Filing and Returns: Regular GST filings are mandatory, and businesses must ensure timely submission of returns to avoid penalties. These returns should accurately reflect all taxable services, including milk chilling and storage.
Conclusion
The inclusion of GST on milk chilling services marks a significant shift in the dairy industry's operational dynamics. While it presents challenges in terms of increased costs, it also offers an opportunity for standardization and improved compliance. As the industry adapts, the focus will likely shift towards optimizing processes and leveraging technology to offset the financial impacts of these tax changes.
💡Facing issues on paying your GST payment? Then download PICE business payment app the solution to make your GST payments easily. Take a demo session now to see how it works for you.



















