GST on Charitable Trust in India
- 30 Dec 24
- 8 mins

GST on Charitable Trust in India
Key Takeaways
- Charitable trusts enjoy GST exemptions for religious, healthcare, and educational services.
- GST applies to commercial activities, non-charitable supplies, and conditional donations by trusts.
- Trusts must register for GST if turnover exceeds ₹20 lakh (₹10 lakh in special category states).
- Compliance includes invoicing, GST returns, record maintenance, and ITC management.
- Professional guidance helps trusts manage GST obligations without hindering their mission.
Charitable trusts have a major function in addressing social issues and welfare activities in India. While these organisations operate on not-for-profit bases, they are not completely outside the realm of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
This blog gives a comprehensive overview of GST on charitable trusts, covering registration, exemptions, and compliance obligations, including the impact of GST on charitable trust activities.
What Is a Charitable Trust?

A charitable trust is an association of people created to provide educational, religious, social, or other welfare services for the public without the intention to make a profit from the service. The trusts basically rely on grants, donations, and contributions to fund their activities.
The state charity organisations are very crucial in supporting the needy while helping with education and different humanitarian causes. Though their main goal is to serve communities, they can perform transactions that relate to GST.
GST Applicability for Charitable Trusts
Under the framework of GST, charitable trusts do not receive automatic exemptions from taxation. GST applicability relies on the type of activities they undertake. According to GST regulations, some activities of the charitable trusts are exempted, whereas others are subject to taxation.
Exempt Activities
The following are the some activities of charitable trusts that are exempted from GST:
- Religious and Charitable Services
Religious and charity trust services are exempted from GST. This includes services of religious institutions like meditation, yoga, or spiritual counseling, as well as activities focused on education promotion, poverty alleviation, or public health improvement.
- Healthcare Services
The charitable institutions offering healthcare services, such as hospitals, clinics or nursing homes established for charitable purposes, are exempt from GST. This also covers diagnostic services, medical treatments, and other services related to health and provided by these trusts.
- Educational Services
Educational institutions operated by charitable trusts which offer services like pre-school education or higher secondary education are exempted from GST. Similarly, educational programs leading to legally recognised qualifications, like degree programs, are also eligible for this exemption.
Taxable Activities
The following are certain activities of charitable trusts that are taxable under GST:
- Commercial Activities
Exempt charitable trusts are any charitable trusts carrying out gross-body activities considered as commercial like rental of premises, conducting of paid seminars or workshops and selling of goods and services which have to pay GST. The most important factor in this analysis is determining whether the activity does anything other than produce charitable income.
- Supply of Goods and Services
If the trust provides any goods or services which are in turn not related to the trusts’ charitable purposes like selling products or consultancy services in exchange for cash, GST is exigible. The trust must charge GST on such transactions and adhere to applicable tax laws.
- Donations with Consideration
Donations that are tied to benefits, like advertising in exchange for sponsorship, are treated as a supply of service and thus attract GST.
GST Registration for Charitable Trusts

Charitable trusts have to analyse their requirement for GST registration depending upon their activity type and turnover. As per the law of GST, any person including charitable trust has to perform an online GST registration if the organisation's aggregate turnover is more than the prescribed threshold limit of ₹20 lakh or ₹10 lakh for states under special category. The aggregate turnover comprises all exempted supplies, export supplies, and taxable supplies made by the trust.
The GST registration process for charitable trusts includes the following steps:
Step 1: Online Application
Access the official GST portal, complete the registration form (GST REG-01), and upload the necessary documents.
Step 2: Verification
The submitted application and documents are reviewed by the GST authorities for approval.
Step 3: GSTIN Issuance
After the verification process is done, a special GST Identification Number (GSTIN) is issued to the trust.
Voluntary Registration
Charitable trusts, even with annual turnover below the threshold limit, can opt for voluntary GST registration. This may be advantageous if the charitable trust has activities that require ITC on the procured goods and services. Voluntary registration will help the trust to lower its tax liability and maintain financial management effectively.
Compliance and Documentation for GST for Charitable Trusts
After completion of GST registration, charitable trusts have to comply with several obligations, including:
- Invoicing: Generating accurate tax invoices for all taxable supplies, which should include the GSTIN, applicable GST rate and the amount charged as GST.
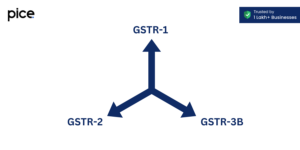
- Filing Returns: Regularly submitting GST returns such as GSTR-3B for a summary return, GSTR-1 for outward supplies, and annual returns. Failure to file returns on time may lead to interest charges and penalties.
- Record Maintenance: Keeping comprehensive transaction records, including donations, sales, purchases, and other income. These data must be retained for a minimum of six years from the annual return filing date.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Properly claiming ITC on qualifying purchases and using it to reduce GST liability. To achieve accuracy, trusts have to guarantee that only the inputs used in the performance of taxable activities can be claimed as ITC.
Impact of GST on Charitable Trusts

The implementation of GST had an impact on India's charitable trusts. While it has streamlined the tax system and enhanced transparency in their financial operations, it has also added to the compliance burden, particularly for trusts involved in both taxable and exempt activities.
For example, a charitable trust managing an educational institution needs to handle GST for activities such as renting out spaces for different functions or providing educational supplies, even though its core educational services are exempt. This necessitates meticulous financial planning and accounting to maintain compliance without undermining the primary goal of the trust.
Challenges and Considerations
Here are some challenges and considerations that charitable trusts need to consider for GST:
- Challenges of Dual Activities: Many charitable trusts operate as taxable and non-taxable organizations hence their compliance with GST is quite tricky. This has been proved to require meticulous record keeping, accurate expense allocation, and a coherent understanding of tax related matters to overcome all the challenges.
- Higher Compliance Load: Following GST’s intricate rules and regulations has increased administrative responsibilities, diverting valuable resources from primary missions.
- Economic Pressure: Including specific activities under the GST framework has raised operational expenses, affecting the funds available for supporting beneficiaries.
- Challenges with Exemptions: Interpreting the complexities of GST exemptions for charitable activities remains difficult, creating uncertainties and potential risks of non-compliance.
- Requirement for Expert Guidance: At various times, it becomes difficult to ensure that all the charitable trusts are in compliance with GST and this may lead to seeking assistance of professionals on the same.
Conclusion
The introduction of GST has undoubtedly brought additional complexity to the functioning of charitable trusts in India. Proper planning, awareness and professional guidance can help charitable trusts handle their GST obligations efficiently.
By doing so, they can continue their mission of serving the community without facing unnecessary financial or legal hurdles related to GST on charitable trust operations.
💡If you want to streamline your payment and make GST payments, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
 By
By