GST Bill Format & How to Make GST Invoice?
- 18 Nov 24
- 12 mins

GST Bill Format & How to Make GST Invoice?
- What Is a GST Invoice?
- What Is the Mandatory GST Invoice Checklist?
- GST Bill Format
- How to Create a GST Invoice?
- What Common Errors Should You Avoid When Making a GST Invoice?
- When to Issue a GST Invoice?
- When Is Issuing a GST Tax Invoice Not Mandatory?
- If an Invoice Is Issued Before GST, Can It Be Revised?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Issue invoices promptly for timely ITC claims.
- Complete all mandatory invoice fields accurately.
- Select the correct invoice type for each transaction.
- Specify the place of supply for correct tax calculation.
- Double-check details to avoid invoicing errors.
A GST invoice is a fundamental aspect of all transactions under GST. Issuing GST invoices helps comply with GST rules and regulations for service providers (suppliers) and recipients.
Non-issuance of invoices can lead to difficulties in claiming input tax credits. Learn how to make GST invoice here in detail.
What Is a GST Invoice?

A GST invoice reflects the transaction record between a buyer and a seller. It includes the details of goods and services supplied and the total amount payable. These invoices help customers understand the structure of goods and services supplied followed by the payments and deductions.
When the total transaction value is more than ₹200, sellers need to issue invoices under GST. It is necessary to generate invoices for legal compliance. The invoices further help customers understand and track the payments, thereby ensuring transparency.
A GST invoice is important for suppliers to claim input tax credit (ITC). ITC reduces the outward tax liability of businesses. Thus, a GST invoice is a crucial component for both the supplier and the customer.
What Are the Types of GST Invoices?
Here are the different types of invoices under GST:
1. Bill of Supply
A registered entity issues a bill of supply while supplying goods and services exempt from GST. A supplier registered under the composition scheme also uses a bill of supply. This differs from a regular tax invoice as it does not contain GST. Thus, a registered entity issues it when they supply taxable and exempt supplies to an unregistered person.
2. Aggregate Invoice
An aggregate invoice is a consolidated invoice of multiple goods and services sold to the same customer with each invoice value not exceeding a specific limit. This reduces paperwork while simplifying invoicing under the GST system. However, this invoice can be used when the transactions occur within the same state.
3. Credit Note
A registered entity needs to issue a credit note when the taxable value of supply needs reduction and when goods are returned. It is a correction to the original invoice when the taxable value or tax levied is more than the tax payable pertaining to a supply.
4. Debit Note/Supplementary Invoice
A debit note, also known as a supplementary invoice, is used to increase the taxable value of supplied goods and services. It acts as a post-sales adjustment or price revision to rectify mistakes in the original invoice for sales. You need to issue this invoice when the taxable value is less than the tax payable.
5. Reverse Charge Invoice
A reverse charge invoice applies under a reverse charge mechanism when the tax liability shifts to the registered recipient of goods and services from the supplier. Governed by the GST regulations, the timeline of these invoices is specified. These invoices should include complete details like nature of supply, tax payable and reason for reverse charge.
What Is the Mandatory GST Invoice Checklist?
Here are the mandatory parameters for GST-compliant invoices, including client details:

- Unique invoice number and invoice issue date
- Customer details like the name and company details
- Shipping and billing address details followed by the contact details, such as email address
- Taxpayer’s and customer’s GSTIN (GST details)
- Details of supply (transaction details) and delivery locations
- HSN code for goods and SAC code for services
- Description of the items you dispatch and the item rate
- The net value of goods and services specifying quantity
- GST rates including the tax amount under CGST, SGST and IGST
- If the reverse charge is applicable
- Discounts and bank details as additional details
- Handwritten or digital signature
However, if the recipient is unregistered and the invoice value is more than ₹50,000, the following factors need inclusion:
- Name and address of the recipient
- Delivery address
- Name of the state and state code
GST Bill Format
Here is the GST invoice format:
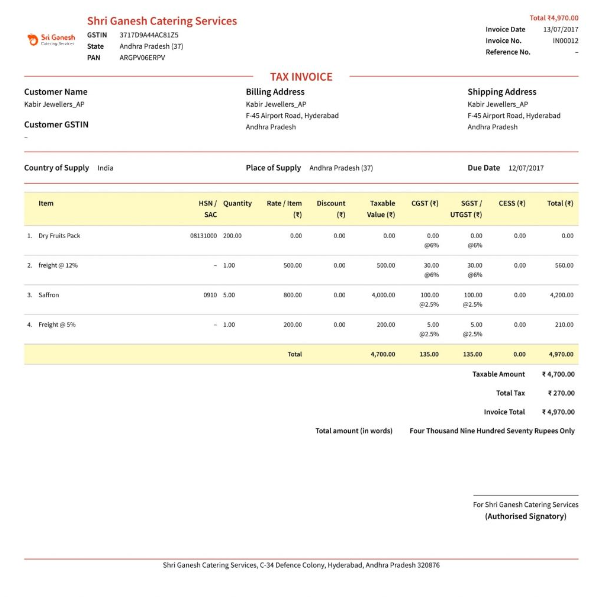
Source: https://razorpay.com/learn/gst-invoice-guide-how-to-create-one/
How to Create a GST Invoice?
You can create a GST invoice manually or using GST invoice software. A client invoicing software can generate invoices automatically when relevant details of sales or outward supplies are entered. Here are the steps to generate a compliant invoice:
Step 1: Select the Option ‘Invoice' (built-in every accounting/GST software)
In case there are multiple branches, you will get an option to choose the branch that will issue the GST invoice.
Step 2: Feed-in Date of Invoice
You need to fill in the invoice date. However, if outward supply is undertaken on a credit basis, you need to fill in the payment date as well. If payment is received on the same day, the payment date and invoice date will coincide. Mentioning the date clarifies the payment terms, payment mode and payment process for recipients.
Step 3: Choose the Debtor/Customer from the List
You need to incorporate the list of customers or debtors to create an invoice. You can select the option ‘Create Debtor/ Customer’ before you choose them from the drop-down tab to prepare the invoice.
Step 4: Choose the Place of Supply
The place of supply determines the type of GST such as IGST or CGST and SGST. Your system will auto-select the place of supply based on the delivery/shipping address. In case the address is not known, the system will select the state in which the supplier is registered.
Step 5: Feed in the Details of Goods or Services
You need to create the list of goods and services by selecting the option ‘Create item’. Further, you need to select the list of goods and services that you need to supply from the drop-down menu.
Step 6: Click to Create GST Invoice
Once you have completed filling in the above-mentioned details, click 'Create GST Invoice' to generate the invoice. You can download the invoice generated in Excel or PDF format from the GST invoice generator to take a print.
What Common Errors Should You Avoid When Making a GST Invoice?

The following are the common mistakes to avoid while preparing an accurate invoice:
1. Incomplete Information
You need to fill in all the mandatory fields in the GST invoice accurately. The mandatory field includes date, invoice number, GSTIN, recipient details and details of goods and services supplied.
2. Incorrect GSTIN
You need to verify the GST identification number (GSTIN) of the supplier and the recipient. Incorrect GSTINs can result in issues pertaining to input tax credits.
3. Mismatched Invoice Numbers
Ensure that the invoice numbering system is sequential and unique. A mismatch in the invoice number or a duplicate invoice number can lead to compliance issues.
4. Mismatch Between Invoice and Supply Date
Your invoice date and supply date need to align to avoid affecting tax liability and reporting.
5. Incorrect HSN or SAC Codes
Use the correct HSN (Harmonised System of Nomenclature) code or SAC (Service Accounting Code).
6. Calculation Errors
Calculate the taxable amount, GST rates and total amount accurately to ensure accurate tax calculations.
7. Missing Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) Information
If the invoice is subject to the reverse charge mechanism under GST, mention the same on the invoice.
8. Inconsistent Invoice Format
Ensure to maintain a standardised and consistent format for the invoices for clarity and understanding.
9. Failure to Mention Place of Supply
For correct tax calculations, make sure to mention the place of supply on the invoice. It will determine the applicable tax rate (GST) under IGST or CGST and SGST.
10. Not Issuing the Correct Type of Invoice
The invoice type varies based on the type of transactions. You might need to issue a bill of supply, debit note or credit note based on the transaction. Ensure you issue the right type of invoice.
11. Late Filing or Issuance
Make sure to file your GST returns and issue invoices within the stipulated timeline. Late issuance or filing may result in penalties and impact the recipient's input tax credit.
12. Non-Compliance with GST Rules
You need to be updated with the latest GST rules and regulations to avoid non-compliance. A lack of compliance can lead to penalties, adverse legal consequences and loss of input tax credit.
When to Issue a GST Invoice?

A GST invoice is a proof of goods and services supplied. It helps the supplier and the recipient claim input tax credit. However, suppliers often face challenges in issuing invoices at the right time. Here is when to issue a GST invoice:
1. Issuing GST Invoice on Goods (Normal)
Section 2 (96) of the CGST Act mandates the issuance of an invoice by a supplier on or before the removal of goods for supply. 'Removal' refers to the moment goods are dispatched for delivery or when the recipient picks them up.
2. Issuing GST Invoice on Goods (Continuous Supply)
For continuous supply in an ongoing business relationship, the supplier must issue invoices before either generating an account statement or receiving payments, whichever occurs first.
3. Issuing GST Invoice on Services
Suppliers of services need to issue invoices within 30 days of service completion. This ensures compliance with GST regulations and helps service recipients claim input tax credits within the right time.
4. Issuing GST Invoices on Bank and NBFC Services
Banks and Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) need to issue GST receipts within 45 days of service completion. The invoice needs to mention the different natures of financial services and their transaction cycles.
When Is Issuing a GST Tax Invoice Not Mandatory?
Here are the conditions under which it is not mandatory to issue a GST tax invoice:
- The suppliers need not issue a tax invoice if the recipient is unregistered under GST.
- If the recipient states that he/she does not require a tax invoice, the supplier does not have to issue an invoice.
However, the above-mentioned criteria need to be met simultaneously to apply for exemption. In case any one criterion is met, the supplier needs to issue a tax invoice. Alternatively, registered suppliers can issue a consolidated tax invoice at the end of each day, listing all taxable supplies made to unregistered recipients.
This procedure is permitted under the GST framework to streamline and simplify the invoicing process for small-value transactions. Suppliers need to adhere to the specified conditions to avoid legal complications and penalties. Adherence to the GST invoicing rules can help claim input tax credits.
If an Invoice Is Issued Before GST, Can It Be Revised?
Revising invoices helps in accurate financial record reporting while impacting applicable taxes and liabilities. It further helps maintain an accurate tax rate and record under the GST regime. Dealers need to obtain provisional registration and convert the same to a permanent registration. Suppliers can revise their invoices within one month from the issuance date of the registration certificate.
According to Rule 53 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017, invoices can be amended to reflect changes in prices and GST rates, whether upward or downward. You can either make changes to errors or mention the changed transaction value or tax amount.
Here are the particulars that a revised invoice needs to have after alterations in GST rates or other changes:
- Mention ‘Revised Invoice’ on the invoice
- Supplier’s name, company address and GSTIN
- A unique and consecutive serial number pertaining to the financial year, not more than 16 characters
- Invoice date
- Recipient’s particulars (including name and address) and GSTIN
- Invoice serial number of original professional invoices (an already-issued GST invoice) and the date against which the revised invoice is being issued
- The supplier’s or authorised person’s signature or e-signature
Conclusion
To answer how to make GST invoice, you need to follow the steps discussed in the blog. This will help you maintain records of the transactions related to the supply of goods and services.
You can use this invoice to claim an input tax credit to offset the output tax liability. Make sure to issue the invoices at the right time to avoid penalties.
💡If you want to streamline your payment and make GST payments, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
 By
By 

















