All About Form DRC 17 in GST
- 16 Jul 25
- 6 mins
All About Form DRC 17 in GST
Key Takeaways
- DRC stands for Demand and Recovery Case, used by the GST department to recover unpaid taxes from defaulters through legal means.
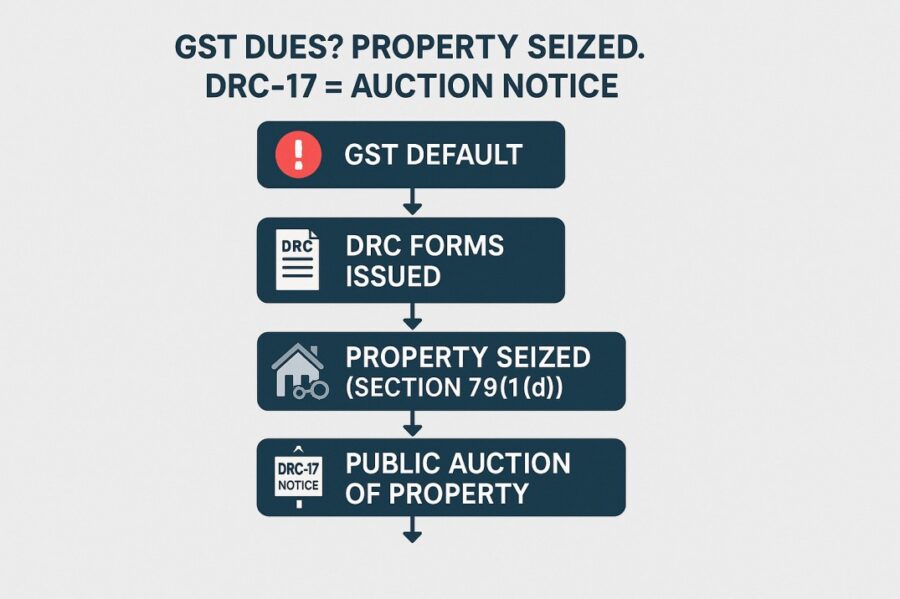
- Form DRC-17 is a statutory notice issued under Section 79(1)(d) of the GST Act for the auction of seized movable or immovable property.
- It includes details like recovery amount, auction schedule, and property specifics to ensure transparency in the recovery process.
- The format of DRC-17 categorizes assets into shares, movable, and immovable properties, each with detailed identifiers for buyers.
- If GST dues remain unpaid beyond 30 days of property seizure, DRC-17 enables lawful auction to recover the pending dues.
The Indian government introduced DRC, or Demand and Recovery Case, to help recover GST dues from taxpayers. There are several DRC forms that help ensure that the GST law is followed by all. This blog will inform you about DRC and one of its specific forms, DRC 17. Moreover, it will also discuss the format of Form DRC 17 in GST, along with other essential information.
Definition of DRC in GST and Its Working

Demand and Recovery Case is a legal procedure through which the tax department of India sends a notice to any business/ individual that has not paid the correct amount of GST. To fulfil different purposes, there are a total of 26 DRC forms. One of these forms is Form DRC 17 in GST.
The government uses DRC to maintain the correct amount of tax collection and prevent tax evasion. In the DRC process, the government can ask for the unpaid GST amount along with additional interest or penalties.
Section 79(1)(d) and Its Relation with Form DRC 17 in GST
Under Section 79(1)(d) of the GST Act, an officer can seize property from a defaulting taxpayer. An officer must follow prescribed rules while doing this. The seized property can be movable or immovable. Generally, an officer can detain property until the person pays their due amount.
The government sells the seized property if the person does not pay within 30 days. After that, the government will use the sale proceeds to recover any unpaid tax amount. They will also recover the costs of seizing and storing the property. The taxpayer receives any remaining amount left after collecting the GST debt.
Form DRC 17 in GST facilitates this process. It serves as a notice for the sale of all/any detained property. It ensures that the officer selling the property follows due process. The government then uses Form DRC 17 to inform the person about the auction of the seized property.
What is DRC-17?
DRC-17 is a form used for providing notice for the auction of immovable/movable property under section 79(1) (d) of the GST Act. It helps the government recover dues legally and efficiently through property sales when taxpayers do not comply. The details that are included in Form DRC 17 in GST are as follows:
- Auction time and date
- Recovery amount
- Details of date, demand order, recovery ID and period
- Quantity of the property scheduled to be auctioned
- Schedule of shares, movable and immovable property
Format of DRC 17 Notice
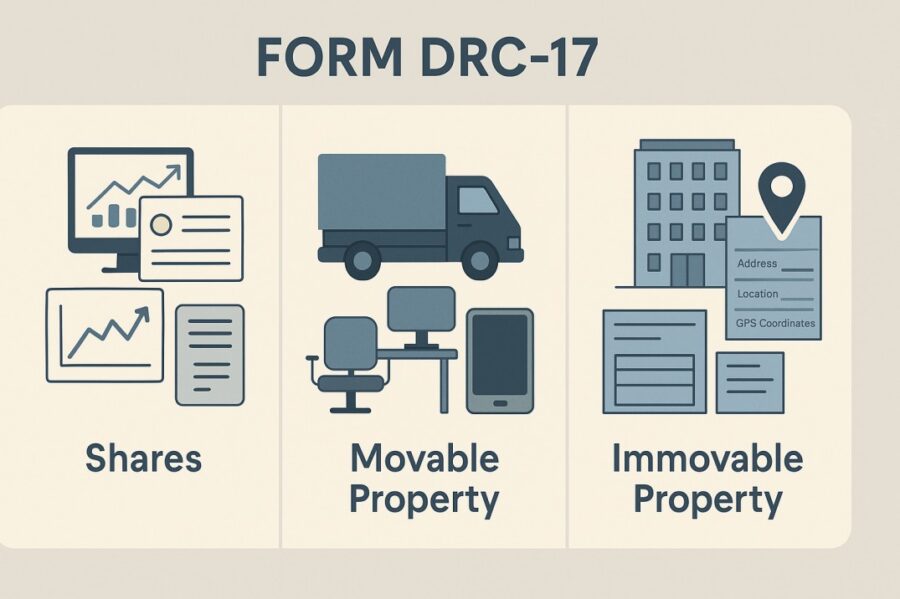
In form DRC 17, there are three kinds of schedules, which are shares, movable, and immovable.
- Shares
This portion deals with financial securities, specifically shares owned by the defaulter. It lists the names of the companies in which the defaulter holds shares, along with the number of shares for each. This enables interested buyers or investors to assess the potential value and investment opportunity during the auction.
- Movable
This part lists all movable goods up for auction. Movable goods refer to items that can be physically transported, such as vehicles, office equipment, machinery, or electronics. For each item, the form mentions its description and the quantity available. This helps potential bidders understand what’s available for purchase and in what volume.
- Immovable
This section contains detailed information about immovable properties, such as land, apartments, or buildings. Specific details like the flat or building number, floor number, and the name of the premises or building identify each property.
The address of the property is further broken down into road or street name, locality or village, district, state, and postal PIN code. Additionally, the form optionally includes GPS coordinates and latitude and longitude for more precise location tracking. This detailed description ensures that there is no ambiguity regarding the details of the property that is up for auction.
For a better understanding, take a look at the official format of form DRC 17:
Conclusion
DRC is useful in cases of any default of payment under GST by a taxpayer, where they pay less than what they owe. There are several DRC forms and one of such forms is DRC 17 in GST. This form contains details regarding the auction of any property seized by the government.
If the taxpayer is not capable of paying the pending GST amount themselves, then the government conducts this auction.
💡If you want to streamline your invoices and make payments via credit or debit card or UPI, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
 By
By 
















