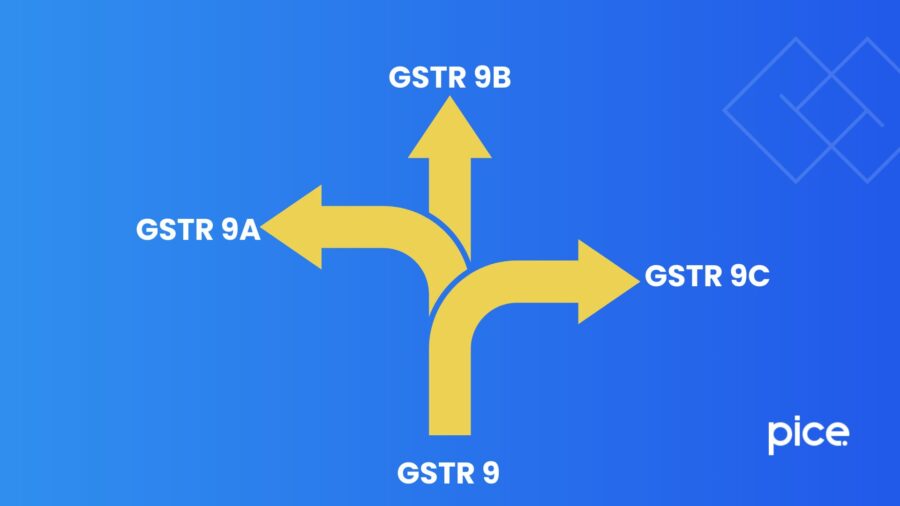
Difference Between GSTR 9, GSTR 9A GSTR 9B and GSTR 9C
- 21 Feb 25
- 6 mins
Difference Between GSTR 9, GSTR 9A GSTR 9B and GSTR 9C
Key Takeaways
- Different Forms for Different Taxpayers – GSTR 9 (regular), 9A (composition), 9B (e-commerce), 9C (audit).
- Filing Deadline – All GSTR 9 forms are due by 31st December of the next financial year.
- Late Fees Apply – Penalties vary based on turnover, with a capped late fee.
- Key Details in GSTR 9 – Covers supplies, ITC, tax paid, and past-year adjustments.
- Certification Rules – GSTR 9C needs CFO certification; others require a digital signature.
Under the GST regulations, different categories of taxpayers have to file annual returns within specific due dates. GSTR 9A, 9B and 9C are different forms under GSTR 9, which taxpayers have to use for filing of GST returns.
However, there are significant differences between GSTR 9, GSTR 9A, GSTR 9B and GSTR 9C. Learn about the differences here to use the appropriate form for GST return filing.
Different Types of Annual Returns Under GSTR 9 Form

Rule 80 of the CGST Rules 2017 (Central Goods and Services Rules) presents the different types of returns under Form GSTR 9 as follows:
● GSTR 9: A regular taxpayer under GST filing returns in Forms GSTR 1, GSTR 2, GSTR 3 and GSTR 3B during a financial year need to file this form.
● GSTR 9A: Composition Scheme taxable persons need to file GSTR 9A.
● GSTR 9B: Electronic Commerce Operators (e-commerce operators) need to file this form.
● GSTR 9C: Taxable persons who need their accounts to be audited under Section 35 of the CGST Act need to file Form GSTR 9C (Audit Form).
Non-Applicability of Annual Return Under GST
The list of taxable persons who do not have to file annual GST returns is as follows:
● Distributors of Input Service
● Tax Collector under Section 52
● Tax Deductor under Section 51
● Non-resident taxable person
● Casual taxable person
Due Date & Penal Provisions
The due date for filing Form GSTR 9 is 31st December of the following financial year. For instance, for the financial year ending on 31st March, 2025, the last date of annual returns filing is 31st December, 2025.
Late filing of the above-mentioned form attracts penalty as follows:
| Taxpayer Turnover Limit | Late Fee Per Day | Maximum Late Fee |
| Up to ₹5 crore | ₹50 (including ₹25 CGST and ₹25 SGST) | 0.04% of the annual turnover in state and Union Territories |
| Between ₹5 crore and ₹20 crore | ₹100 (₹50 CGST and ₹50 SGST) | 0.04% of the annual turnover in state and Union Territories (0.02% under CGST and SGST respectively) |
| Above ₹20 crore | ₹200 (₹100 each for CGST and SGST) | 0.50% of annual turnover in Union Territories and states (0.25% under CGST and 0.25% under the SGST Act) |
Information to Be Furnished in Annual Return (GSTR 9)

The table below illustrates the details furnished in GSTR 9 annual returns:
| Part | Details to Be Furnished |
| I | Basic details such as financial year, GSTIN, Trade name and legal name (if applicable) |
| II | Information pertaining to outward and inward supplies during a specific financial year |
| III | Details pertaining to input tax credit (ITC) as furnished in returns filed during the financial year |
| IV | Details of tax paid as mentioned in returns filed during the specific financial year |
| V | Includes details of previous financial year transactions that taxpayers declared in returns for April to September of the current financial year |
| VI | Other Details such as details of taxes paid like GST refunds, demands, HSN-wise details of goods received and supplied, late fees paid and payable, categorisation of different inward supplies, details of outward supplies based on HSN |
Comparison of GSTR 9, GSTR 9A, GSTR 9B and GSTR 9C
The table below presents a detailed comparison between Forms GSTR 9, GSTR 9A, GSTR 9B and GSTR 9C:
| Factors | GSTR 9 | GSTR 9A | GSTR 9B | GSTR 9C |
| Nature | GSTR 9 return is the consolidated form for all monthly/quarterly returns | Annual return form for composite taxpayers | Summary of total sales, details of advances, claims for input tax credit and tax collected during a financial year (acts as a financial statement) | GSTR 9C reconciliation statement is an analytical statement pertaining to GST returns that a CFO or Finance Head has to self-certify |
| Who Should File | GST registered taxpayer | Composition Taxpayers | e-Commerce Operators | Taxpayers registered under GST with aggregate annual turnover exceeding ₹5 crore |
| Not Applicable to | Composition dealers, non-resident taxable persons (NRTP), casual taxable persons (CTP), input service distributors, Unique Identification Number (UIN) holders, persons paying TCS and TDS, Online Information and Database Access Retrieval (OIDAR) Service providers | Non-resident taxable persons, casual taxable persons, input service distributors, TDS payers under Section 51, e-commerce operators paying TCS under Section 52 | Input service distributors, non-resident taxpayers, casual taxpayers, taxpayers under the Composition Scheme, persons paying TDS | Similar to exclusions for Form GSTR 9; however including registered persons with annual aggregate turnover not exceeding ₹5 crore |
| Late Fee and Penalty | Varies based on the aggregate annual turnover as mentioned in the penalty section mentioned above | ₹200 per day (₹100 each under SGST/UTGST and CGST) | ₹200 per day (₹100 each under SGST/UTGST and CGST). Penalty will keep accumulating until they reach 0.25% of the e-commerce operator’s total turnover. | A general penalty of ₹25,000 |
| Who Needs to Attest or Certify | Taxpayers need to attest it using a digital signature | - | - | The CFO or Finance head needs to certify using a digital signature |
Conclusion
The differences between GSTR 9, GSTR 9A, GSTR 9B and GSTR 9C are significant across multiple factors. For instance, the category of taxpayers who should file each of these forms differs. The purpose for filing these forms is further different for applicable taxpayers.
However, the due date for filing all these forms is 31st December of next year for a particular financial year. Ensure you file the returns (as applicable) within the due date to avoid paying late fees and penalties.
💡If you want to streamline your payment and make GST payments via credit card, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
 By
By