What Is An E-Invoicing System Under GST: Components, Benefits, Compliance & Generation
- 13 Nov 25
- 10 mins

What Is An E-Invoicing System Under GST: Components, Benefits, Compliance & Generation
Key Takeaways
- The e invoicing system is now mandatory for businesses with annual turnover above ₹10 lakh from April 2025, making GST compliance easier.
- Using an e invoicing system reduces human errors, improves accuracy and ensures real-time authentication of B2B transactions.
- A robust e invoicing system auto-populates GST returns, helping businesses avoid penalties and compliance risks.
- The e invoicing system accelerates payment cycles by enabling faster invoice processing and better cash flow management.
- Adopting the e invoicing system saves time and costs by eliminating manual data entry, paperwork and repetitive reconciliation tasks.
When starting a company, many people struggle to maintain compliance with the GST law. Invoicing is one of the key aspects where they face issues.
A simple way to reduce invoice-related discrepancies is by switching to a GST-compliant electronic invoicing or e-invoicing system. Effective April 2025, most small businesses with an annual aggregate turnover exceeding ₹10 lakh will also be required to adopt e-invoicing.
Hence, it is essential to invest in a robust e-invoicing software and learn how to generate bulk invoices effectively. Details about the same have been discussed here.
What is e-Invoicing Under GST?
The GST Council introduced e-invoicing for easier authentication of B2B transactions and faster processing of related documents. Originally, the e-invoicing system was designed for large companies as per the 35th GST Council Meeting.
However, to ensure systematic management of accounts payable and accounts receivable, all businesses now crossing ₹10 lakh in annual aggregate turnover are required to follow the 30-day e-invoice rule.
This works much like a GST-registered business generating an e-way bill when transporting goods from one location to another.
When you analyse a standard e-invoice, you find the data not to be visually appealing. However, these can be rendered efficiently by software or converted further into easily understandable visual e-invoice formats.
This invoicing system helps curb tax evasion with real-time data checks, speeds up GST return filing and enhances accuracy by reducing manual errors.
Mandatory Components of an e-Invoice
Altogether, there are 30 separate fields in a standardised electronic invoice, each one of them needs to be addressed by the current taxpayers. Here's how:
| E-Invoice Data/ Invoice Information | Description of the Field |
| Document code | It is a specific type code that identifies each document category |
| Supplier GSTIN | Includes a supplier’s GST Identification Number |
| Legal name of the supplier | The name must match with the respective supplier’s PAN |
| Supplier address | It should have the full address line of the supplier |
| Place of supplier | Declares the supplier’s town, village or city |
| Supplier state code | Helps verify a supplier’s state with a specific code |
| Document number | It features a sequential invoicing number for commercial purposes |
| Supplier PIN code | Reflects the 6-digit postal code of the supplier |
| Previous invoice date and reference | It may include documents like a credit note, which directs towards the original invoice |
| Document date | It is simply the invoice issuance date |
| Recipient's name | Has to specify the purchaser’s official name as per PAN |
| Recipient's GST Identification Number | Basically, a buyer’s GSTIN |
| Recipient's state code | In terms of GST, it is crucial for determining the place of supply |
| Address of the recipient | Shows the complete address of the buyer |
| Place of supply by state code | It is a code that denotes a recipient’s state |
| Pincode | This is the buyer’s 6-digit Pincode |
| Recipient’s location | This can be the buyer’s village, town or city |
| IRN or Invoice Reference Number | It is a unique number issued by a GSTIN and is shared with the buyer |
| Shipping to GSTIN | In this section, one finds the GSTIN of the customer receiving the shipment |
| Shipping to state, pincode and code | Points to the postal and state codes relevant for the supply of specific commodities and services |
| Place, address and name under ‘Dispatch From’ | It contains the legal name of the dispatching agency along with its address |
| Supply type code | It verifies whether the supply type is B2B, SEZ, etc. and gives the relevant code |
| Item description | This area has detailed information about the supplies listed in the invoice |
| HSN code | It will have the Harmonised System of Nomenclature codes listed for the sold services or goods |
| Item price | It constitutes the per unit price of an item, excluding the GST component and after applying discounts (if added) |
| GST rate | As per the GST rules, the applicable rates for a sold item or service can be nil, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28% |
| Assessable value | It is the GST-excluded invoice value after allowing discounts (if given) |
| IGST value, CGST value and SGST value | It has a thorough breakdown of the entire applicable GST |
| Total value of the invoice | Finally, you must declare the gross invoice amount, inclusive of GST |
💡If you want to streamline your payment and make GST payments via credit, debit card or UPI, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
5 Benefits of an e-Invoicing System
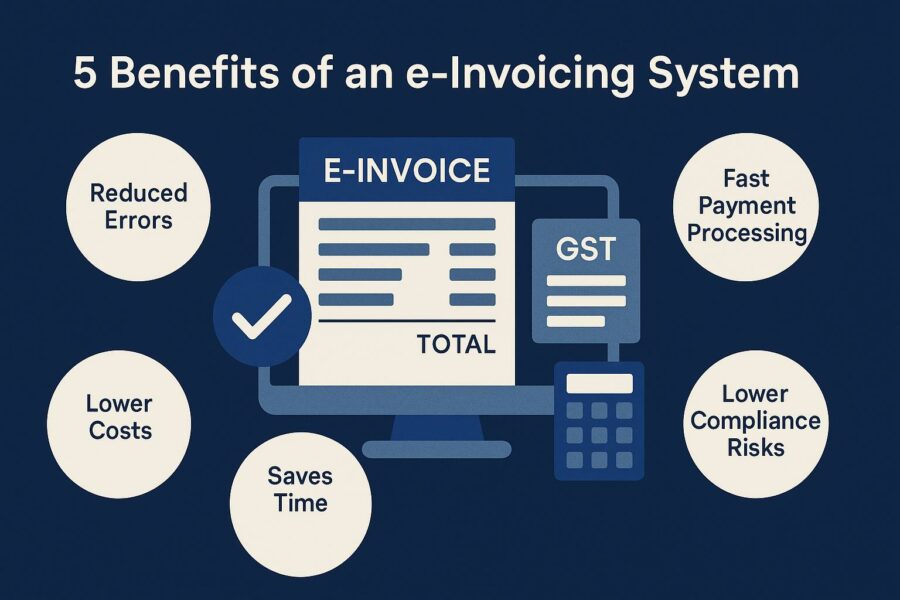
Electronic invoicing enables automatic matching and verification of 3 key documents: purchase orders, invoices and shipping receipts. It is significantly more beneficial than traditional invoicing. Here's why:
1. e-invoicing Helps Reduce Human Errors
Electronic invoicing is a game-changer for Indian businesses. Not only does it streamline routine tasks, but it also minimises the chances of errors while recording transactions. It directly enhances the relationship with clients as your company faces fewer disputes.
2. e-invoices Help Reduce Costs
You can cut off the costs that were incurred earlier on printing, paper and postage. In the long run, it shows major savings on operations and logistics.
3. Companies Benefit From Fast Payment Processing
The invoice processing takes place faster as the system is undoubtedly more efficient. As a result, you can enjoy improved cash flow and the instances of late payments will consequently be reduced.
4. You Have Lower Compliance Risks
The procedure of e-invoice issuance makes sure that a business complies with the latest GST rules. This happens as the tax amounts for various supplies are auto-populated. Therefore, unlike traditional invoices, e-invoices offer real-time validation of transactions. This access to verified transaction data by tax authorities helps in curbing fraudulent activities.
5. Electronic Invoicing Saves Time
E-invoicing eliminates the need for repeated manual data entry, as the data is directly shared between systems and government portals. It helps your business when it comes to managing finances.
Besides, the global e-invoicing market is anticipated to expand at a rate of 17.7% between 2024 and 2032. This visibly states the widespread adoption of e-invoicing and business process automation. Therefore, if you want to meet the dynamic compliance requirements and grow your business, now is the right time to invest in reliable GST invoicing software.
What are the Main Compliance Requirements of the e-invoicing System?
The e-invoicing system comes with a set of compliance requirements aimed at ensuring authenticity, integrity, accuracy and adherence to regulations under the GST law. Here are the key points to keep in mind:
1. Authenticity of Origin: It is crucial that the e-invoice clearly shows who the sender is, confirming that it truly comes from the stated issuer. This is typically done using advanced electronic signatures or secure digital certificates.
2. Integrity of Content: The information on the invoice needs to stay unchanged from the moment it is issued until it is cleared. If there is any tampering, the invoice becomes invalid and digital signatures play a key role in spotting any unauthorised alterations.
3. Standardised Formats: E-invoices should be created and submitted in specific formats (like JSON or XML), ensuring all mandatory fields are included, such as the invoice number, date, details of the seller and buyer and tax information.
4. Mandatory Data Elements: Invoices must include certain data fields as required by local laws, such as process identifiers, payment instructions, VAT breakdown and details for each line item.
5. Security and Accessibility: Data must be encrypted both during transmission and while stored, and only compliant digital formats are accepted for legal and business purposes.
Failing to comply can lead to invalid invoices, penalties and disruptions in business operations. For instance, if you enter incorrect invoicing details, it can lead to a fine of ₹25,000 per invoice. Similarly, if your business surpasses the threshold and yet fails to generate e-invoices, you can face penalties of ₹10,000 per invoice.
What are the Different Steps Involved in an e-Invoice Generation?
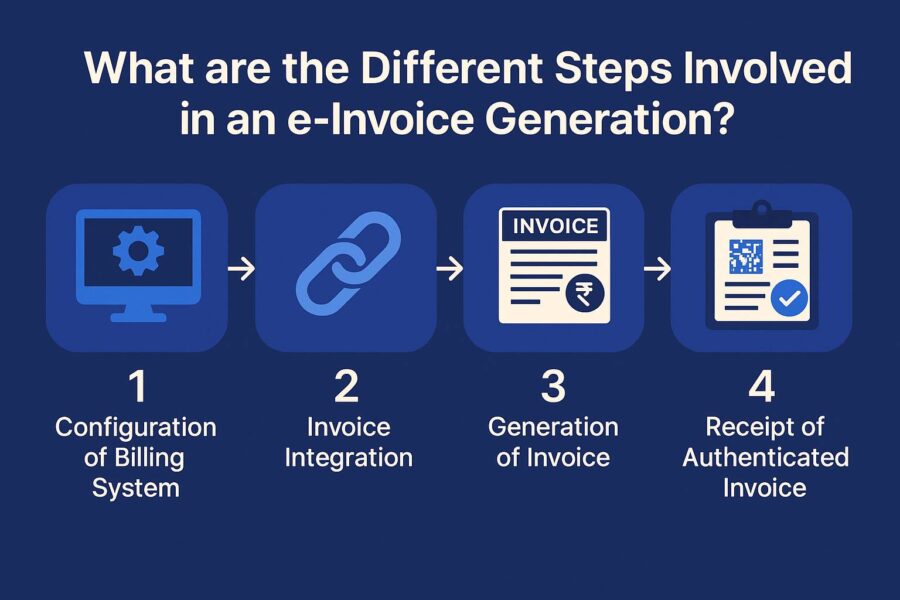
Generating and receiving e-invoices include multiple steps as follows:
Step 1: Configuration of the Taxpayer’s Billing/ ERP System
First, you must ensure that your GST billing software is aligned with the latest PEPPOL standards. Normally, the CBIC notifies the updated e-invoice schema. To incorporate any changes, you need to have thorough communication with your software provider.
Step 2: Invoice Integration Through a Valid Method
Typically, all taxpayers get two main methods to link with the IRP or Invoice Registration Portal, which is managed by the GST Network. You can either opt for a direct API integration or choose a bulk upload tool.
Step 3: Generation of the Invoice
Finally, in the third step, you generate the invoice by utilising your professional billing software. Here, you must include several key details like the mandatory details about the supplier and recipient, item details, invoice value and more.
Step 4: Submission of Data to IRP Portals
For uploading all the relevant invoice details, you can:
- Provide the JSON file issued by your invoicing tool
- Upload particulars of B2B invoices via a GSP or API connection
- Present information by using an integrated app
Additionally, the IRP supports mobile-based or SMS-based uploads to ensure taxpayers’ convenience.
Step 5: Receipt of Authenticated Invoice
Following validation, you get the authenticated e-invoice, including the IRN and QR code, from the IRP. Provided that you have already added an email, you will receive a confirmation through email as well.
Step 6: Verify the Auto-Population in GST Returns
The GST portal and e-way bill portal receive the updated invoice particulars from IRP to auto-populate the GSTR-1 return. This automates tax return updates, simplifying compliance and minimising manual work.
Time Limit to Generate e-Invoice
Indian businesses need to issue an e-invoice through the Invoice Registration Portal no more than 30 days from the date quoted on the corresponding debit notes, credit notes or invoices. This means all invoices issued on July 11th, 2025, must be reported to the IRP by August 10th, 2025. All registered businesses have to mandatorily follow this 30-day time period to ensure compliance with GST rules.
The e-invoicing system was introduced to ensure precision and efficiency in the billing process. Companies can thus rely on this procedure to correctly report business proceedings in their GST returns. Moreover, getting your submissions in on time really helps make the process of claiming input tax credits much smoother and reduces the likelihood of running into problems during audits.
Conclusion
Embracing the e-invoicing system under GST is no longer optional for most small businesses. It is essential for compliance, efficiency and growth. By adopting robust e-invoicing solutions, you will minimise errors, streamline tax reporting and ensure smooth GST returns, positioning your business for success in India’s rapidly digitising economy.
 By
By