What Is Article 279A GST Council?
- 16 Sep 24
- 9 mins

What Is Article 279A GST Council?
- What Is the GST Council?
- What Is Goods and Services Tax?
- Why Do We Need a GST Council?
- How Is the GST Council Structured?
- GST Council Recommendations
- Key Features of the GST Council
- Background of the Goods and Services Tax Council
- Role of the GST Council
- Importance of the GST Council
- Duties of the GST Council
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- The GST Council under Article 279A, brings Union and State governments together on GST matters.
- GST consolidates multiple indirect taxes into a single, simplified national system.
- The Council sets tax rates and ensures uniform GST implementation across states.
- Simplifying tax compliance boosts economic growth and aligns India with international markets.
- Regular Council meetings tackle challenges and shape the future of India's GST framework.
Introduced through the 101st Constitutional Amendment Act in 2016, the establishment of the GST Council has the authority to make recommendations to Union and State governments on GST issues. It serves as a platform where Central and State governments work to create an effective and uniform framework of GST. This council was established under Article 279A.
In this blog, we will explore Article 279A GST council, the importance of the Council, its impact on the economy and other important aspects associated with it.
What Is the GST Council?

Goods and Services Tax Council, also known as GST Council, is a body formed by the President of India. Came into effect on September 15, 2016, the Council provides administrative suggestions when the union or the state government consults on GST issues.
What Is Goods and Services Tax?
Goods and Services Tax is one of the crucial indirect taxation reforms in India, introduced with the principle of 'One Nation, One National Market'. Earlier, there were multiple indirect taxes at different stages of the supply chain that had to be paid. GST eases out the taxation system by subsuming all indirect taxes under one head, becoming a single taxation system led to a national common market.
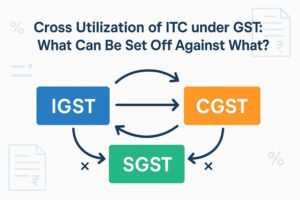
It also eliminates the cascading effect of double taxation and reduce high compliance cost. The 3 components of GST include CGST, SGST and IGST. CGST and SGST facilitate intra-state trade. On the other hand, IGST facilitates inter-state trade.
Why Do We Need a GST Council?
From making, administering, amending and executing the laws, the GST Council is responsible for all the regulations concerning GST. The Council comprises Finance Ministers from all states and is headed by the Union Finance Minister of India.
The Council is the primary body responsible for all decisions about GST. It regulates GST rates, exemptions, deadlines for annual returns and so on. It is the prime responsibility of the GST Council to maintain special provisions and a fixed tax rate for all the states.
How Is the GST Council Structured?
Article 279(1) of the Indian Constitution lays down the structure of the GST Council. It states that the Council should be a joint forum between members of the union and the state government. The members of the GST Council will include:
- The Union Finance Minister of the country is the Chairperson of the council.
- The Union Minister of State would be a member of the council accountable for the Revenue of Finance.
- The other members of the GST Council include one minister from the state government who administers finance or taxation. The state government can also appoint one minister of their own choice as a member of the GST Council.
GST Council Recommendations
Article 279A(4) empowers the GST Council to provide recommendations to all states and Union Territories on matters relating to GST. These recommendations cover issues like the goods or services against which GST can be charged. It also helps the state government decide on exemptions from GST.
The GST Council also determines the rate of tax for goods and services. Some of the major decisions taken by the GST Council are over matters such as the following:
- Rate of GST
- Special rate of GST for a few specific states
- Regulating the applicable GST rates during natural calamity
- Place of supply
- Threshold limits
Key Features of the GST Council
Given below are some of the features of the GST Council:
- The GST Council office is in New Delhi, India.
- The Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) is a chairperson in every meeting of the GST Council. The CBEC is a non-removable, permanent, non-voting invitee present in all of their sittings.
- The Revenue Secretary of India holds the position of the Ex-officio Secretary in the Goods and Services Tax Council.
- The Additional Secretary of the GST Council is a post that is equivalent to the Additional Secretary of the Indian Government.
Background of the Goods and Services Tax Council
The introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) ensured a standardised and centralised taxation system with a uniform tax rate across all states. The Article 279A entrusted the President with the authority to form the GST Council.
In September 2016, the President ordered the establishment of the GST Council. The Secretariat of the Council would be located in New Delhi, India and the Union Revenue Secretary would be the Ex-officio Secretary to the Council.
Role of the GST Council
Some of the important responsibilities of the GST Council are listed below:
- Determining Tax Rates: The primary responsibility of the Council is to determine tax rates for various goods and services. It can also set more than one tax rate for the items according to the nature of the goods or services.
- Authorisation of GST Laws: The Council gives the final verdict on matters like the implementation, procedure for GST registration, tax payments, GST filing of returns, etc.
- Addressing and Overcoming GST Issues: The GST Council addresses complaints and challenges faced in the course of implementation of GST. It meets regularly to ensure smooth administration.
- Tracking GST Implementation: The GST Council has a constant track of the effect of GST implementation in the country.
Importance of the GST Council

The Council has a significant contribution towards the economic growth of the country. It ensures smooth business transactions by simplifying the rate structure. Some of the key benefits that it brings along are:
- Smooth Tax Compliance: The Council has simplified the taxation procedure, necessitating one centralised tax on goods and services, which has contributed contributed to promoting tax compliance.
- Alignment with the International Market: It aims towards making laws that are in alignment with international trade.
- Proper Planning: The Council maintains a uniform rate for goods and services.
- Availment of Input Tax Credit: The tax burden of businesses has been reduced significantly with the GST council's provision to avail Input Tax Credit for Goods for tax paid on all purchases. Additionally, the composition scheme has helped small businesses as well.
Duties of the GST Council
The Council is responsible for executing some vital duties. However, the two primary duties of the GST Council are as follows:
- GST Council Recommendations: The Council is authorised to provide recommendations on GST implementation to both Central and State Governments. Some of these recommendations are:
- The Council recommends implementation dates of GST for certain petroleum crude products.
- It also provides recommendations on GST rates for specific states. During natural disasters, the GST Council recommends special rates.
- If a certain state undergoes loss of revenue due to the implementation of GST, the Council recommends compensation. The Parliament takes the final decision and gives it to the State government.
- GST Council Meetings: The Council meets regularly to further facilitate the taxation method of GST. In these meetings, it decides several things:
- The Council decides over the taxes and additional cesses paid to the Central and State Governments to be subsumed in the GST levied.
- It also makes laws, lays down procedures of principles of levy, and collection of GST for transactions crossing state borders.
- The Council determines rates of GST along with floor rates and bands. It also establishes threshold turnover limits for exemptions.
Conclusion
Article 279A is key to fostering cooperation between the Union and State Governments and shaping the GST framework in India. The Goods and Services Tax Council continues to play a crucial role in making decisions for applicable tax rates, addressing challenges and facilitating the taxation process that lays down the path for a brighter economic future in India.
💡If you want to streamline your payment and make GST payments, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
 By
By