What is HSN Code in GST: Structure & Importance
- 17 Oct 25
- 9 mins

What is HSN Code in GST: Structure & Importance
Key Takeaways
- HSN code is a globally standardised system developed by WCO for classifying goods in taxation and trade.
- In India, HSN codes are 8 digits long, where the last two digits specify tariff details for accurate classification.
- HSN helps determine the correct GST rate for goods, ensuring compliance and error-free tax filing.
- It simplifies invoicing and documentation, eliminating the need for lengthy product descriptions.
- Over 200 countries use HSN codes, promoting transparency and uniformity in international trade.
Product classification is essential for smooth GST compliance in India. Under GST, one such classification system is the Harmonised System of Nomenclature (HSN) code. It helps standardise the identification of goods for taxation.
To clearly understand what is HSN code in GST, it is important to explore its full form, structure, and how authorities use it to determine applicable GST rates. Thus, this article will provide you with a detailed overview of the HSN code, including its definition, format, and category-wise listings.
What is the HSN Code in GST?

HSN, or Harmonised System of Nomenclature, is a uniform classification system that the World Customs Organisation (WCO) made to group products internationally. To systematically group the goods, there is a standardisation of the classification of items under chapters, sections, subheadings, and headings.
By this classification, a six-digit code is generated for an item. In this six-digit code, two of each digit reflect the chapter, heading, and subheading. As India has been a member of WCO since 1971, it uses HSN codes, which were introduced in the country in 1986.
India uses HSN codes to classify items for Central and Customs Excise. India adds two more digits to differentiate its commodities in either Customs or Central Excise. This makes the codes more specific and also makes the HSN codes an eight-digit code.
Why is HSN Important?
The reasons why HSN codes are important are as follows:
- Classification of Products: Classifying their products becomes easier for businesses, and it helps them accurately calculate taxes and streamline necessary operations.
- GST Rates Classification: To group a product in a specific category of GST slab rates, the HSN codes play a vital role. This helps in business compliance with GST regulations.
- Compliance for GST Invoicing: HSN codes come in useful when it comes to the systematic classification of goods for the GST invoicing process.
- Tax Calculation: The importance of HSN codes for GST compliance comes from the fact that they are very useful in the accurate classification of goods. This categorisation helps in easy and accurate tax calculation by identifying the correct GST rate.
- Simplification of Documentation: In the past, businesses needed to provide a detailed description of goods when filing for taxes. Now with HSN codes, these detailed descriptions are not necessary, which simplifies the documentation process.
- Utilisation of Data: HSN codes not only help businesses but also the government. Its uses range from policy-making and revenue collection to data analysis and economic decision-making.
- Enhancement of Understanding: As HSN codes are standardised ways of recognising an item, they help tax authorities and businesses to properly categorise and identify the goods.
HSN Worldwide
More than 200 economies and countries use HSN, which is an international classification system to streamline their taxation and trade. All over the world, with a base of 98%, classification of global goods is done with the use of HSN codes for promoting smooth international trade.
Its use is possible as it facilitates:
- Simplification of tariffs and customs leads to simple and easy export and import procedures.
- Worldwide adoption due to its simplicity.
- Governments and organisations aid to access international trade data easily and efficiently to help with their international trade statistics.
- Consistent and detailed classification to avoid confusion across international markets in coding and naming goods.
- Code variations for some countries provide flexibility regarding the proper classification of goods based on the nature of goods.
HSN in India
India joined the World Customs Organisation (WCO) in 1971. Initially, Indian authorities used 6-digit HSN codes to classify commodities for Customs and Central Excise purposes. To improve accuracy, Customs and Central Excise later added two more digits, creating an 8-digit classification system.
HSN Code List for GST India
In India, the categorisation of goods is done in sections, chapters, and headings. All of these add up to make an HSN for a single product. The table below provides a list of goods classification in the Indian GST regime:
| Section | Chapter | Commodities | HSN Code | GST Rates |
| I | 01-05 | Animal products and live animals | 0101-0511 | 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% |
| II | 06-14 | Vegetable products | 0601-1404 | 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% |
| III | 15 | Vegetable or animal oils and fats | 1501-1522 | 5%, 12%, 18% |
| IV | 16-24 | Beverages, spirits and vinegar; prepared foodstuffs; tobacco | 1601-2403 | 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28% |
| V | 25-27 | Mineral products | 2501-2715 | 5%, 12%, 18% |
| VI | 28-38 | Products of the allied or chemical industries | 2801-3825 | 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28% |
| VII | 39-40 | Rubber and its articles, and plastics and their articles | 3901-4017 | 12%, 18% |
| VIII | 41-43 | Skins and raw hides, fur skins and their articles, and leather | 4101-4304 | 5%, 12%, 18% |
| IX | 44-46 | Wood and its articles, cork and its articles, and straw items | 4401-4601 | 12%, 18% |
| X | 47-49 | Paperboard, paper, wood pulp or pulp of other fibrous cellulosic material | 4701-4923 | 12%, 18% |
| XI | 50-63 | Textiles and their articles | 5001-6310 | 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% |
| XII | 64-67 | Footwear, umbrellas, headgear, walking sticks, sun umbrellas, seat sticks, riding crops and their items, and whips | 6401-6702 | 12%, 18% |
| XIII | 68-70 | Glass items, ceramic products, glassware, stone articles, cement, plaster, mica or similar materials, and asbestos | 6801-7020 | 12%, 18% |
| XIV | 71 | Cultured or natural pearls, precious metals, precious or semi-precious stones, metals layered with precious metal, precious metal articles, coins, and imitation jewellery | 7101-7118 | 0%, 3%, 5%, 12%, 18% |
| XV | 72-83 | Base metals and their articles | 7201-8311 | 5%, 12%, 18% |
| XVI | 84-85 | Mechanical appliances and machinery, electrical equipment, and mechanical parts | 8401-8548 | 5%, 12%, 18% |
| XVII | 86-89 | Aircraft, vehicles, vessels, and associated transport equipment | 8601-8716 | 12%, 18%, 28% |
| XVIII | 90-92 | Watches and clocks; and optical, musical, photographic, cinematographic, measuring, precision, checking, surgical, or medical instruments and apparatus | 9001-9209 | 12%, 18% |
| XIX | 93 | Ammunition and arms, and their accessories and parts | 9301-9306 | 12% |
| XX | 94-96 | Miscellaneous manufactured articles | 9401-9617 | 12%, 18% |
| XXI | 97 | Antiques and collectors’ pieces, and works of art | 9701-9706 | 12% |
Structure of the HSN Code in India
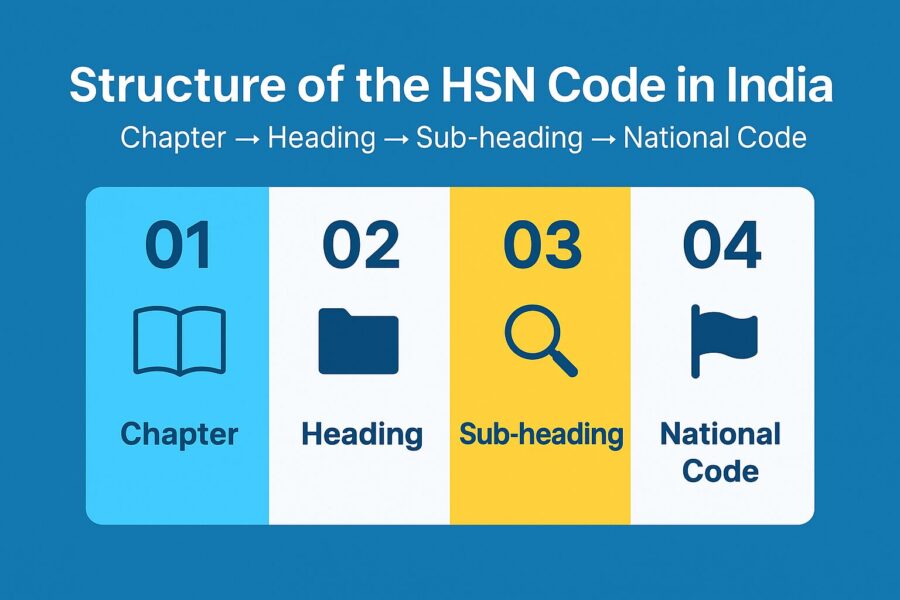
The structure of an HSN code contains 21 sections, 99 chapters, 1244 headings, and 5224 subheadings in India. It so happens that these 21 sections are classified into 99 chapters, which are further divided into 1244 headings, followed by a 5224 subheadings division.
Within the 6-digit code, the division and marking are as follows:
- The first two digits of the code from the left represent the chapter in which the good belongs.
- The next two digits from the left represent the heading in which the good belongs.
- The next two digits from the left, which are the final two digits of the six-digit HSN code, represent the sub-heading in which the good belongs.
In some countries, including India, the government puts two additional digits at the end of the code to help classify the product more accurately. These last two digits reflect the tariff items. This results in an 8-digit HSN code.
Working of HSN Code with Example
HSN code plays a crucial role as an identifier for more than 5000 commodity groups under the Indian GST regime. It efficiently categorises goods in an orderly manner.
For instance, cast iron pipes have an HSN code, which is 7303.0010. The following breakdown of this code provides a better understanding:
- 73, which are the first two digits of the code, demonstrates the chapter for ‘articles of iron and steel’ in which this product belongs.
- 03, the next two digits denote the heading, which is ‘pipes and tubes’.
- 0010, which are the final four digits, further denote the division of this item to a specific type, which is ‘cast iron pipe’.
This is how HSN in GST works to ensure precise classification of goods, thus promoting smooth taxation processes.
Conclusion
A clear understanding of what is HSN code in GST is vital for ensuring accurate GST compliance, streamlined invoicing, and efficient business operations in India. These codes not only simplify tax calculations and documentation but also support uniformity in global trade.
By exploring the full form, structure, and classification system of HSN codes, businesses can reduce errors and enhance transparency in their transactions.
As the GST regime continues to evolve, staying informed about how to apply and interpret HSN codes effectively becomes essential. Leveraging this classification system properly ensures smooth tax filing, better regulatory compliance, and improved operational efficiency.
💡If you want to streamline your payment and make GST payments via credit, debit card or UPI, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.
FAQs
What is the full form of HSN in GST and why is it used?
How is the HSN code structured in India?
The first two digits denote the chapter,
The next two digits denote the heading,
The next two digits denote the sub-heading, and
The last two digits are additional Indian tariff details.
This detailed coding ensures accurate product categorisation for Customs, Central Excise, and GST purposes.
Who needs to mention HSN codes on GST invoices?
Turnover above ₹5 crore: 4-digit HSN mandatory
Turnover up to ₹5 crore: 2-digit HSN (optional for B2C)
Using the correct HSN code ensures proper tax classification, prevents mismatches during GST filing, and supports compliance verification by authorities.
 By
By 

















