Credit Card Acquirer Vs Issuer: Differences, Roles & More
- 21 Oct 25
- 7 mins
Credit Card Acquirer Vs Issuer: Differences, Roles & More
- Key Differences Between Credit Card Acquirer and Credit Card Issuer
- What are the Responsibilities of a Credit Card Acquirer?
- What are the Responsibilities of a Credit Card Issuer?
- Roles of Credit Card Acquirer Vs Issuer: How Do They Work?
- Role of Acquirer and Issuer in Credit Card Chargeback Scenario
- Here is a brief overview of the process that takes place:
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- The credit card acquirer serves merchants by processing and routing payments, while the issuer serves customers by approving or declining transactions.
- Acquirers facilitate transactions between merchants and banks, whereas issuers authorize payments and provide credit to customers.
- The acquirer handles merchant-related risks such as chargebacks and fraud, while the issuer manages customer credit risks and disputes.
- Once a payment is authorized, the issuer releases funds to the acquirer, which then deposits them into the merchant’s account, ensuring a seamless transaction.
- Both entities play crucial roles in chargeback resolution. The issuer initiates and verifies disputes, while the acquirer manages communication and funds return on behalf of the merchant
As of the year 2024, India has over 100 million active credit cards in circulation. However, did you ever wonder how the whole payment processing system works?
When a cardholder initiates a credit card payment, there is a series of processes that rapidly take place, seemingly within seconds, to facilitate a smooth commerce.
In this article, we will discuss the credit card acquirer vs issuer, two primary entities that play an important role in the credit card payment ecosystem.
Key Differences Between Credit Card Acquirer and Credit Card Issuer
The number of credit card transactions per month reached 300 million in 2024. This whole credit card transaction ecosystem is actually facilitated by both the primary credit card merchant acquirer and the credit card issuer.
However, there is a fair share of credit card acquirer vs issuer differences:
| Aspect | Credit Card Acquirer | Credit Card Issuer |
| Customer Served | Merchant (You) | Cardholder (Customer) |
| Primary Role | Facilitates and processes payments | Approves or denies credit card payments |
| Form of Communication | Sends payment transaction requests to the issuers through payment processors | Responds to authorisation requests and validates outcomes to the acquirer |
| Risk Exposure | Responsible for fraud from merchant side, chargebacks and PCI-DSS compliance | Responsible for credit cardholder risk, handling disputed transactions |
What are the Responsibilities of a Credit Card Acquirer?
The credit card acquirer is also referred to as the merchant bank or acquiring bank. They play an important role in facilitating credit card transactions between merchants and cardholders.
- Facilitating Smooth Card Transactions
- The main job of a card acquirer is to facilitate all card-based payments for various businesses.
- After the customer swipes their card online and pays with it, the acquirer immediately gets to routing that transaction in a secure manner.
- They facilitate the payment to the credit card network and then to the issuing bank.
- This maintains a smooth payment flow from authorisation to settlement without any hindrances.
- Effective Handling of Transactions Routinely
- Acquirers are solely responsible for routing information of payments to appropriate card payment networks like Mastercard, RuPay and then finally to the issuer.
- They manage this data processing quickly and securely to reduce any latency and make efficient authorisation decisions.
- A smooth routing process leads to a better payment experience for customers.
- Representation of Merchants
- Credit card acquirers are not just middlemen; they also represent businesses in the world of digital payments. It includes management of merchant accounts, overseeing of chargebacks, help with dispute resolution and ensuring PCI-DSS compliance.
- The acquirer essentially speaks of a business when communicating with issuers, payment processors and card networks.
💡Pay your credit card bills in an easy and secured way and experience smooth transactions with the PICE App.
What are the Responsibilities of a Credit Card Issuer?
The credit card issuer is the issuing bank and plays an important role in the payment ecosystem by providing credit to cardholders. The issuing banks primarily focus on serving customers and managing risks that come with lending credit.
- Issuance of Credit and Debit Cards
- The credit issuer is the institution that provides credit cards to customers on behalf of networks like Mastercard, Visa, etc.
- They enter into agreements with concerned cardholders and then issue payment cards to the authorised consumers.
- Ensuring Secure Transfer of Funds
- During the initiation of a credit card payment, funds are transferred from the issuer bank to the acquiring bank.
- The credit card issuer ensures that payments get successfully processed and the merchant receives all funds.
- Facilitating Approval and Rejection of Transactions
- The credit card issuer validates the legitimacy of initiated transactions on the part of customers.
- They check whether the cardholder has enough credit limit available.
- Their role is critical in protecting customers from unauthorised usage and helps merchants avoid any kind of invalid payments.
- Responsible Management of Customer Accounts
- Credit card issuers are responsible for the management of cardholder accounts.
- A few such instances are setting limits, determining interest rates and implementing security protocols to protect the information of cardholders.
Roles of Credit Card Acquirer Vs Issuer: How Do They Work?
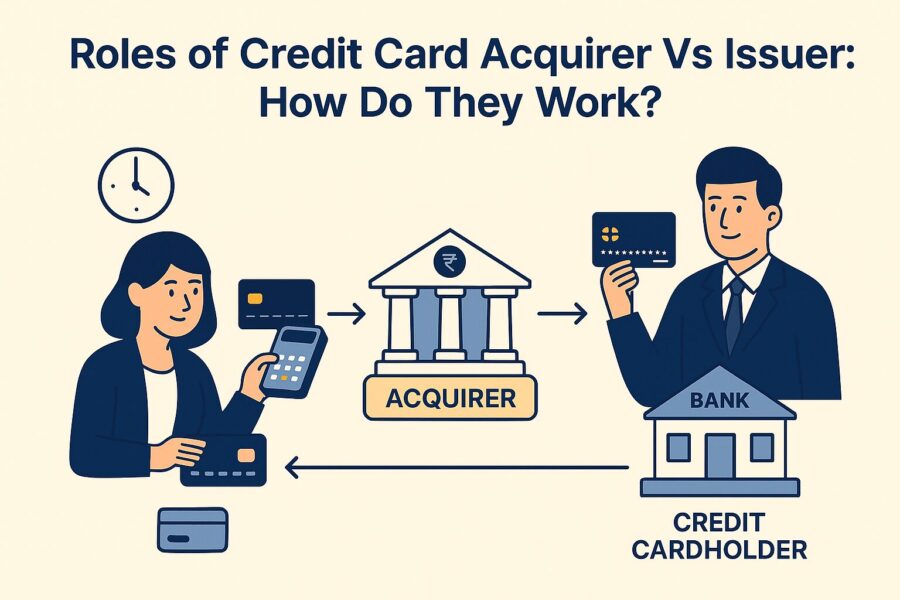
- Initial Request of Authorisation
The transaction begins with an authorisation request. This happens when a customer purchases something with a credit card.
A merchant, upon getting this request, sends it directly to the 'Acquiring Bank'.
- Role of Acquiring Bank
These banks are responsible for the smooth facilitation of payments made with credit cards and initiating transactions on behalf of merchants.
They get the authorisation request from the merchant and send it for approval to the issuing bank.
- Role of Issuing Bank
Issuing banks are important as they directly face customers in the payment cycle. They make an issue of credit cards to the customers and are responsible for setting credit card limits, levying charges of interest and fees, dispute resolving, to name a few.
- Transaction Completion
After the approval of a transaction, the acquiring bank then deposits funds into the accounts of merchants and customers get charged for purchasing.
Note: While the involvement of two banks sounds complex, both of them are required to ensure the legitimacy of the payment process. They ensure that both parties are satisfied.
Role of Acquirer and Issuer in Credit Card Chargeback Scenario
Did you know that for most industries, a business having a chargeback rate above 1% is considered highly risky? This creates a negative impression of these merchants and they become more likely to face penalties from card networks and processors.
Credit card issuers and acquirers both play key roles in the management of chargebacks. This is a persistent issue these days for merchants who operate online.
There are scenarios when customers ask for a refund (in the form of a chargeback) on their credit card statement. It may happen when they are unhappy with the service or product they purchased from a business.
Here is a brief overview of the process that takes place:
- After a customer initiates a chargeback, they contact the issuer (bank) to dispute a charge.
- The ‘dispute’ then gets investigated by the bank.
- If it is found to be legitimate, the chargeback process gets started for customers.
Conclusion
The working relationship of the credit card acquirer vs issuer, in spite of their different roles, is what ensures a smooth commercial credit card payment process. It ensures that a purchase or return is processed efficiently and successfully.
Knowing the differences between the two is vital for businesses that are aiming to thrive in the dynamic landscape of business payments.
 By
By