What is the Difference Between a Proforma Invoice and an Account Sales?
- 24 Nov 25
- 12 mins
What is the Difference Between a Proforma Invoice and an Account Sales?
- Proforma Invoices Vs Account Sales
- What Essential Information Is Included in Proforma Invoices Vs. Account Sales?
- When to Use Proforma Invoices Vs. Account Sales?
- Proforma Invoice Meaning
- Account Sales Meaning
- How Proforma Invoice Works?
- How Account Sales Works?
- Advantages & Disadvantages of a Proforma Invoice
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Account Sales
- Which Is Ideal: Proforma Invoice vs Account Sales?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the difference between proforma invoice and account sales helps businesses manage pre-sale and post-sale documentation accurately.
- A proforma invoice provides an estimated cost before a sale, whereas account sales record actual sales after goods are sold.
- Proforma invoices are not legally binding, while account sales are legally enforceable records.
- Proforma invoices support quotations, negotiations, and advance payments, while account sales are essential for consignment transactions.
- Knowing the difference between proforma invoice and account sales ensures clear communication, fewer errors, and better financial tracking.
Are you one of the 66% of small businesses that struggle with efficiently managing their financial documents? Financial professionals and business owners often get confused between a proforma invoice and accounts sales, both of which are crucial documents within the business sphere.
They have distinct purposes and knowing the difference between proforma invoices and accounts sales is important to ensure that you handle your transactions accurately.
This blog shall dive into the differences between the two and how you can use them to have a full impact on your business.
Proforma Invoices Vs Account Sales

If you are a business owner, you might have come across both proforma invoices and account sales but knowing what they mean can be tricky. Though they may appear similar, each serves a distinct purpose in the business process.
Take a look at the key differences between proforma invoices and account sales:
| Feature | Proforma Invoice | Account Sales |
| Meaning | It is a preliminary invoice that mentions the estimated costs that were sent before the actual sale was made. | It is a document provided by the agent/consignee; it mentions details about the actual sales made on the seller’s behalf. |
| Objective | Before the actual sale is finalised, an estimate is provided to the buyer. | It extends a summary of commissions, sales and expenses for the sales made on another party's behalf. |
| Timing | It is issued before the sale/goods' shipment to provide an estimate of cost. | It is issued after the goods are sold, usually after the conclusion of a consignment transaction. |
| Content | It includes an itemised list of goods or services, estimated taxes, rates and shipping information. | This includes product descriptions, sales summary, sold quantities and values, sales rate, commissions and other deductions. |
| Legal Status | It serves as an estimate and is not legally binding. | It is legally binding because it confirms that the actual sales have been made and payments are owed. |
| Use Cases | It is used for extending quotations, negotiations or to request payments in advance. | It is common in consignment transactions where agents/third parties sell products. |
| Terms of Payment | As per the arrangement, it may or may not include the terms of payment. | It has the payment details listed, including expenses, commission rates and net proceeds, which go to the seller in question. |
What Essential Information Is Included in Proforma Invoices Vs. Account Sales?
Before you start using proforma invoices or account sales in your business, it is important to know what details each document includes.
While a proforma invoice gives an estimate before a sale, an account sales statement records the actual transaction after goods are sold. Here's a quick comparison:
| Account Sales Items | Proforma Invoice Items |
| Sales summary & total amount | Estimated price of goods/services |
| An itemised list of goods that are sold | A placeholder itemised list of goods/services |
| Commissions that are earned by the agent | Estimated taxes & shipping costs |
| Any further expenses incurred | Terms & conditions of payment |
| Net proceeds that are payable to the principal | Delivery dates & terms |
| Payment information & due date | Buyer’s information & address |
When to Use Proforma Invoices Vs. Account Sales?
A proforma invoice is sent before a deal is confirmed, while account sales come into play after the goods are sold. Knowing when to use a proforma invoice vs an account sales statement can make your business transactions smoother.
Given below is a quick overview that will help you decide:
| Scenario | Proforma Invoice | Account Sales |
| Quotations | A proforma invoice can be used to provide a cost estimate before finalising a sale. For instance, say a buyer requests a quote for a bulk order. In that case, the proforma invoice shall mention the anticipated prices. | It is not applicable. Account sales are not in use for the initial quotation stage. |
| Confirmation of Sales | A proforma invoice is usually not used to confirm sales. | An account sales document may be used after a sale is concluded. For instance, an agent may be selling goods on a principal’s behalf. They would have to issue an account sales document in order to summarise the transaction/commissions earned. |
| Payments to be Made in Advance | One may issue the proforma invoice at the time of requesting advance payments on the basis of estimated costs. For instance, a supplier may send over a proforma invoice to request a certain amount to be deposited before shipping off custom-made items. | It does not apply to this case. Account sales are used once the sale is complete, not for advance payments. |
| Consignment Sales | Does not apply | One may use the account sales document for the sales made on consignment, which details commissions, sales, and incurred expenses. For example, a consignment shop may issue an account sales document to the item owner summarising details about the sales activity/commissions. |
Now that you understand the key differences between a proforma invoice and account sales, what they include and when to use them, let’s take a closer look at each document in detail.
Proforma Invoice Meaning
Proforma invoice, essentially, is a preliminary sales bill that is sent over to buyers prior to any services/goods being delivered. This bill mentions the transaction information that can be expected upon initial glance. This includes the following:
- Estimated prices
- Terms of payment
- Shipping details
In the case of international trade, a proforma invoice is typically used to serve as a reference. It helps buyers get an idea about the prices before settling on their final buys.
Account Sales Meaning
Account sales is a statement consisting of all details as extended by consignees to the consignors in the context of consignment businesses. It informs the consignors about the sales activities, which include information regarding the following:
- The goods sold
- Quantities of sold goods
- Goods’ prices
- Commissions
- Expenses
The account sales document allows the consignors to track the performance and revenue generated from the consigned goods.
How Proforma Invoice Works?
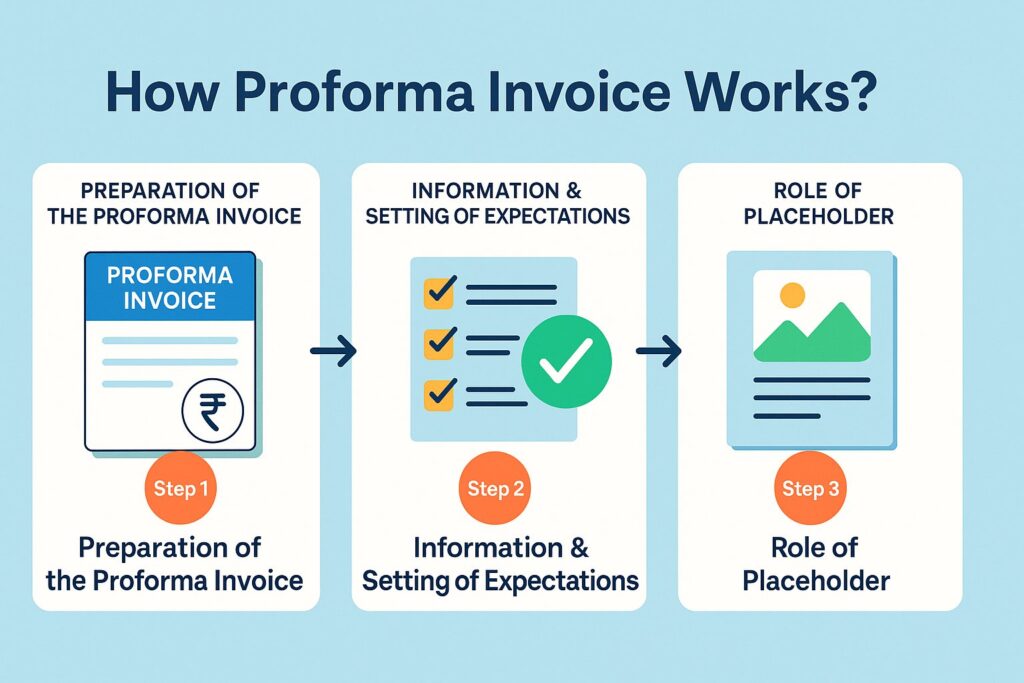
Step 1: Preparation of the Proforma Invoice
Upon an order being placed, a seller formulates a proforma invoice. For the records, this document serves as a 'placeholder'. It highlights the terms, anticipated prices and other conditions prior to the delivery of goods/services.
Step 2: Information & Setting of Expectations
A proforma invoice establishes what the expectations shall be for the parties that are going to be involved in the transaction. It shall include important information like product descriptions, estimated prices, quantities and dates of delivery. A level of transparency makes room for queries to be raised, that a buyer may be faced with regarding the prices/delivery hour.
Allowing Negotiation
A proforma invoice opens up scope for negotiation by presenting a highly informative estimate of pricing. This document lets both the buyer as well as the seller, analyse and adjust the conditions/pricing, prior to settling upon the final deal. It allows both parties to agree beforehand.
Step 3: Role of Placeholder
Up until the issuance of the last, binding invoice, the proforma document serves as the “placeholder” within the accounting records of the seller. It acts as a point of reference in regards to the transaction that is supposed to take place. This document helps with setting and managing assumptions/the entire planning process.
How Account Sales Works?
Step 1: Sales Execution
A consignee/an agent sells goods on the principal's (seller's) behalf. The process shall involve handling of the sales, management of consumer interactions and ensuring that the transaction has been completed.
Step 2: Documentation
Post-sale, the agent shall prepare the document for the account sales. The document will include information about:
- The items sold
- Sales costs
- Commissions earned
- Expenses incurred
Step 3: Compilation of the Summary
The document for account sales shall summarise the information regarding various sales-related activities, while keeping a record of transactions made. This document even features a section mentioning the commissions/fees breakdown that the agent charges.
Step 4: Submission
The document for account sales is completed and then given to the concerned principal. It will extend an elaborate record of the sales concluded, as well as any costs pending in regards to the principal.
Step 5: Reconciliation
The concerned principal shall review the document for account sales. This step will help establish precision. Potential issues/discrepancies may be addressed beforehand. Payments will then be processed on the basis of the terms mentioned in the documents.
Step 6: Payment
The respective principal shall settle the payments as per the terms mentioned in the document for account sales. It shall call for paying off the commission of the concerned agent as well as covering additional expenses.
💡For your bill payments and tracking business transactions, use the PICE App.
Advantages & Disadvantages of a Proforma Invoice
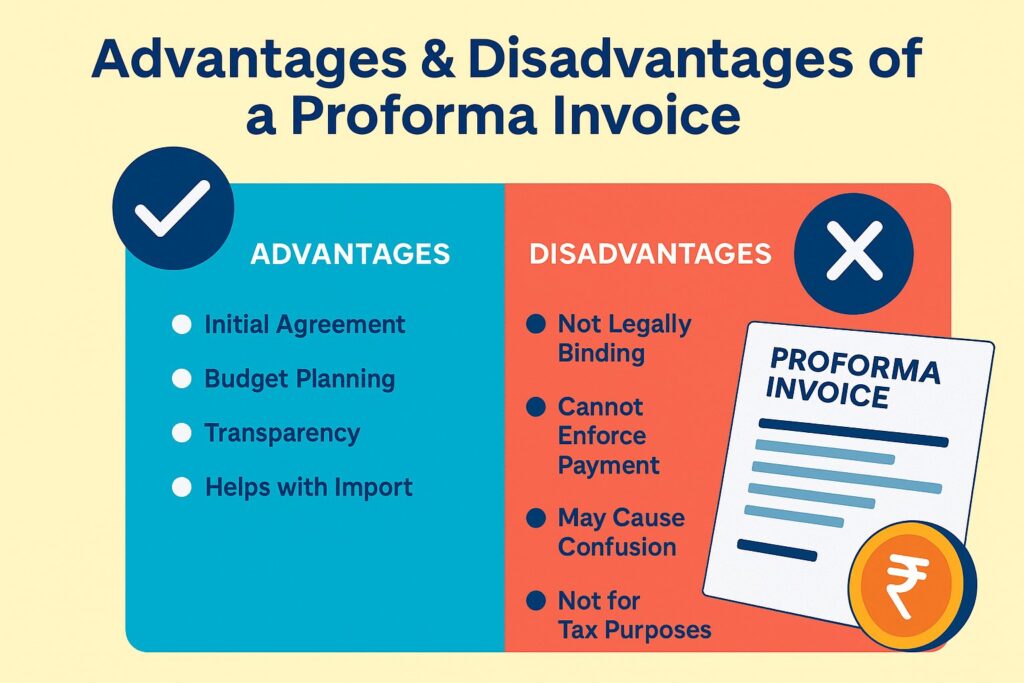
Here are the advantages of a proforma invoice:
- The proforma invoice is not the final bill. One may adjust the contents, be it the quantities, rates, or payment terms, on the basis of negotiations/altering scenarios.
- It allows both parties to arrive at a state of agreement prior to a real sale being made.
- The proforma invoice allows enhanced planning/budgeting efforts in regards to buyers as well as sellers.
- This document serves as the rough document at the preliminary stage. It provides buyers with an outline of what they can expect in the context of conditions and costs.
- The proforma invoice is particularly beneficial for enterprises which have to arrive at decisions/get hold of funds prior to any transaction being settled upon with finality.
- In the context of internationally occurring trade, the importance of the proforma invoice is prominently highlighted. It allows the buyers to have an understanding of the associated prices.
- The information featured on the proforma document may be important to get the required permits for import/financing-related arrangements, accordingly.
However, note that there may be certain disadvantages associated with the proforma invoice, like:
- The proforma invoice does not have any legal standing. Opposed to a legally-binding GST invoice, the proforma invoice does not, by law, necessitate the purchaser to pay.
- It cannot enforce payment on the buyers’ end. This may cause confusion in case the buyer in question decides not to go forward with the purchase initially settled upon.
- If the scope of the proforma invoice is not communicated clearly, it might be assumed to be the final and binding invoice. This shall result in misunderstandings/delays.
- The proforma invoice shall not be used for tax purposes. One cannot claim VAT/GST on the basis of a proforma invoice.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Account Sales
Here are the advantages of opting for account sales:
- For the business, sales records serve as the “unified ledger”. It allows for simplified, efficient and quick access to the details of transactions across departments.
- By having an accurate record of sales, transparency is boosted.
- It establishes a sense of trust between the internal and external stakeholders; as well as with the organisation as a whole.
- Records of sales from the years bygone help new leaders (including senior managers, directors, etc.) go through the transition process with ease.
- Account sales documents make the process of compliance with the record-maintenance rules and regulations an easier task to manage.
- Data in regards to historical sales allows executives to understand sales trends. This enables the business heads to keep track of, as well as predict and chalk out potential growth prospects of the organisation, in the future.
On the other hand, here are certain disadvantages of account sales:
- For large-scale businesses/multinational corporations, the management of records can become quite complex. It will require extensive calculations as well as reporting processes. This may lead to higher costs.
- If any error is detected, it shall take a considerable amount of time to review the associated sales data and correct it.
- Large-scale businesses may have to hire teams to record and monitor transactions daily. This may lead to significant additional salary expenses.
- Even with the installation of automated software, errors may occur during data entry, leading to risks of a compromised record-keeping process.
Which Is Ideal: Proforma Invoice vs Account Sales?
During the process of documenting sales, the type of document one needs depends on the stage of sales they are at. If you are in the pre-sale stage, use a proforma invoice to highlight the proposed prices, terms and conditions and the delivery-related information. This shall help settle upon and streamline the sales procedure further.
If you have completed the sales under an agreement, use the document for Account Sales. This shall mention the finalised sale outcome keypoints, which will include the following:
- Selling price
- Applicable deductions
- Net amount payable to the consignor
It will act as a legally binding record for any parties involved. Go for the right document to make sure of seamless transactions and transparent communication with consignors as well as customers.
Conclusion
To conclude, knowing the difference between proforma invoices and accounts sales is important for businesses so they can manage their financial transactions with more precision. While proforma invoices act as preliminary agreements, account sales represent the actual transactions made.
By recognising the distinctions, businesses shall be able to streamline their invoicing processes, minimise errors and improve their financial record-keeping system. Whether one is a small business owner or a financial professional, being familiar with such concepts will help simplify and navigate complex transactions with confidence.
 By
By 
















