Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor vs Merchant Account: Explained
- 21 Oct 25
- 7 mins
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor vs Merchant Account: Explained
Key Takeaways
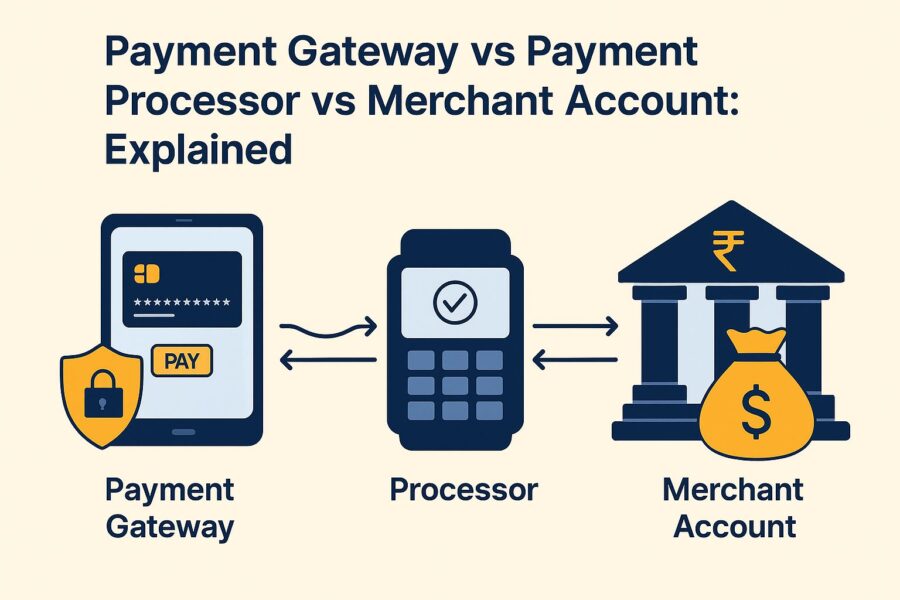
- The payment gateway encrypts and transmits payment data, the payment processor verifies and transfers funds, while the merchant account temporarily holds them before settlement.
- Payment gateways provide encryption and fraud prevention measures, ensuring that customer data remains safe during online transactions.
- Payment processors streamline communication between customers, banks, and businesses, reducing delays and improving transaction speed.
- Having a merchant account is crucial for businesses to receive and manage card payments efficiently, offering faster fund settlements.
- A seamless combination of a payment gateway, processor, and merchant account ensures a secure, fast, and user-friendly payment experience for both merchants and customers.
Did you know that digital payment volume in India rose to 18,737 crore in FY 2023-24, with a CAGR of 44% since FY 2017-18? With increasing online transactions, it becomes essential to know what components are at play behind the scenes to increase business efficiency.
You might have heard of ‘payment gateways’ while making online payments. It works with payment processors and merchant accounts to complete debit and credit card transactions.
This article provides differences between payment gateway vs payment processor vs merchant account, so you can understand their functions, whether it comes to receiving or making payments.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor vs Merchant Account: Major Differences
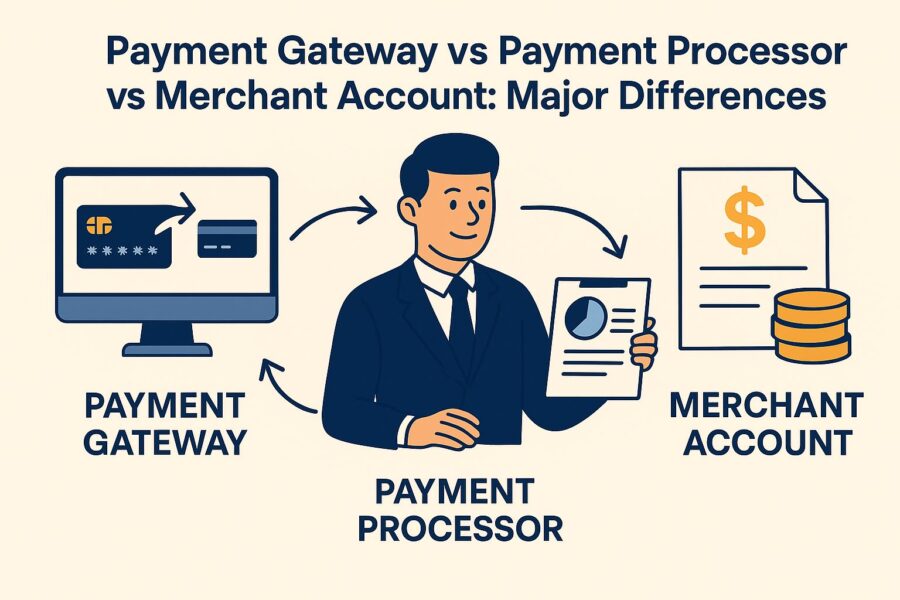
| Factors | Payment Gateway | Payment Processor | Merchant Account |
| Purpose | Encrypts customer payment information and transmits it for authorisation | Handles authorisation and processing of transactions | Temporarily holds the funds from these authorised transactions |
| Role in Transaction Process | Sends payment details safely between the customer, the business and the processor | Authorises payments and transfers funds securely between banks | Holds card funds temporarily before moving them to the main account |
| Merchant System Integration | Offers easy setup through APIs, plugins and modules | Often needs a merchant account and a complex setup | Requires a dedicated account with a bank or provider |
| Services Scope | Mainly transmits payment data without extra services | Provides fraud checks, chargeback handling and compliance support | Stores funds securely until transfer to the business account |
What are Payment Gateways?
Payment gateways are an integral aspect of any virtual terminal. They work by collecting the details of a customer’s credit card data and sending it to the payment processor. Many times, these gateways include a page for purchasing where the customers are able to submit all of their information securely.
Payment gateways were primarily introduced because the payment processors were slow in shifting to web connectivity and were less secure. Thus, the payment gateways provided multiple businesses with fast connections to the web. Therefore, payment gateways work very well with processors and provide a better point-of-sale technology.
There are two primary types of payment gateways: integrated payment gateways and third-party payment gateways.
Benefits of Payment Gateways
- Security: Offers customers/clients a safe and secure place to enter all of their card information. It encrypts all of their data and helps in fraud detection.
- Communication with Processor: Sends the customer information to the payment processor automatically. This allows for double-checking of the information before confirming the transactions.
- Buffer Time: Provides a buffer that the merchant/ businesses can use to resolve any payment information-related issues. Acts as a final cushion before declining or accepting the client's payment.
💡If you are a GST-registered business, use the PICE App for timely payments.
No Must Reads Available
What are Payment Processors?
Payment processors refer to services or companies that enable the process of fund transfer from a customer to a business. Think of it as a mediator that is responsible for communicating messages between:
- Your customers
- Your business
- Your customers’ card brand networks
- Your merchant account
- Your customers’ bank accounts
It works for transactions that involve credit or debit card payments. The role of a processor is to authorise and verify the transaction information in the most efficient and secure way.
You can think of it like a process similar to check clearing. Just like all the checks you receive are submitted to the bank for verification and validation before you receive the payment.
Benefits of Payment Processors
- Market Expansion: Payment processors enable companies to accept a range of payment methods. This facilitates potential expansion of the market.
- Faster Payment Process: They make the process of managing payments faster and help in streamlining the financial operations of a business.
- Connection with Merchant Account: This enables faster financial transaction processing and reception of funds by the business to their merchant account.
What are Merchant Accounts?

Merchant accounts are special kinds of bank accounts that make it possible for businesses to receive transaction funds temporarily without using cash. Similar to what payment processors process, merchant accounts are also capable of taking debit and credit card payments.
When a business has a merchant account, it uses it to hold the payment before transferring it to its business bank accounts after settling the electronic payments. The reason why it is different from a general bank account that a business has is that a merchant account can not be used for tasks such as direct withdrawals and deposits.
The transfer of funds from merchant accounts to business bank accounts takes anywhere from 1 to 30 days. Generally, it is done within 5 business days.
Benefits of Merchant Accounts
- Unified Deposit: The account groups all of the transactions that happened in a period and then transfers them to the business's bank account at the end of the period as a single unified deposit.
- Buffer Account: It acts as a ‘money pot’ where the business is able to keep the funds that they receive for a short amount of time. This highly reduces the payment processing time in case of any refunds.
- Fraud Protection: Before the funds are directed towards the business bank account, it is checked for fraud, which prevents any kind of future hassle, along with saving money and time over a period.
Coordination and Working of Payment Gateway, Payment Processor and Merchant Account
- Customer Starts Transaction: The buyer enters card details on the checkout screen.
- Payment Gateway Encrypts Information: The gateway protects payment data and sends it securely to the processor.
- Payment Processor Checks Request: The processor reviews details with the bank to confirm funds and fraud prevention.
- Issuer Approves Payment: The bank issues a code, the processor and gateway relay it and the business gets confirmation.
- Merchant Account Stores Money: The authorised funds move into the merchant account until transfer.
- Payment Processor Completes Settlement: The processor shifts batched funds from the merchant account to the business bank account.
No Must Reads Available
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between payment gateway vs payment processor vs merchant account is vital for businesses setting up a digital payment ecosystem. While the gateway secures and transmits data, the processor verifies and moves funds, and the merchant account temporarily stores them. Each of them serves a unique function and together they create a safe, seamless business and customer experience in payments.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
Can a business operate without a merchant account?
Is a payment gateway necessary for online businesses?
Can a payment gateway and processor be the same company?
Is a payment gateway more important or merchant account?
No related articles found.
No related posts found.
 By
By 






